In drawing up estimates (calculations) of the investor and contractor, various methods can be applied, and in particular: resource, resource-index, basic-index, etc.
The choice of the method of making estimates (calculations) is carried out in each case, depending on the conditions of the contract and the general economic situation.
The resource method is the calculation in current (forecast) prices and tariffs of resources (cost elements) necessary for the implementation of a design solution. Calculation is carried out on the basis of the requirements expressed in natural meters for materials, products, structures (including auxiliary, used in the manufacturing process), data on distances and methods of their delivery to the construction site, energy consumption for technological purposes, operating time of construction machines and their composition, labor costs of workers. The indicated resources are allocated from the composition of the project materials of various regulatory and other sources.
The resource method is the calculation in current or forecast prices of the cost of all resources necessary for the implementation of an investment construction project.
Resource-index method is a combination of a resource method with a price index system for resources used in construction.
The base-index method is the use of a system of current forecast prices in relation to the value determined at the base level or at the current level of the previous period.
In the base-index method, the cost of work and costs at the base price level is multiplied by the corresponding coefficients - conversion indices.
The cost of work is determined on the basis of the volume of work and unit rates. (unit rate - the cost of direct costs for the work meter).
Unit prices may be federal (EPER-84, SniR-91, RMO, FER-2001), territorial (EPC-99, TER-2001) and company.
Estimation using the indicated prices is carried out at the base and current price level.
The basic level of EPEP and RMO is the price level at 1.01.84, SNiR-91 - at 01.01.91, FER-2001 - at 1.01.00, EPC-99 - at 1.07.99, TEP-2001-at 1.01.00.
Currently, the following types of estimated resource prices are used:
- Actual current estimated prices according to the data of accounting, warehouse and production accounting of enterprises;
- the average territorial current estimated prices according to the calculated data of the RCCS, other independent regional centers, published in monthly collections (catalogs) of estimated prices (“StroyCena”, etc.);
- average prices for basic building materials in the northwestern regional weekly Stroyka.
These methods give different calculation results, i.e. The estimated cost calculated by these methods varies. Therefore, the construction organization should be very careful in choosing the method of calculating the estimated cost of construction, based on specific conditions and potential opportunities. The value of the contract price for construction, which will subsequently be paid by the investor (customer), depends on the results of the calculations. Therefore, the fact of whether the construction organization will receive profit, and therefore its future activity, depends on the degree of adequacy of the costs incurred and the amount of regulatory profit included in the estimated cost of construction.
When making estimates for construction work, the contractor and investor often use several methods to determine the estimated cost, based on the economic situation, as well as the specific conditions of the contract.
There are several common methods for compiling estimated cost:
- analogue
- time-based;
- basic compensation;
- basic index;
- resource index;
- resource.
Resource method costing is reduced to a phased summation of the resources necessary for the construction of a specific design solution in current or forecasted prices, values \u200b\u200band tariffs. As for the calculation, it is carried out on the basis of specific indications presented in natural meters of demand for resources, products, designs and materials.
It also provides information on the distances to the construction site, offers options for transporting building materials, connecting to energy, describes the estimated labor costs of workers. Consumption and varieties of the listed resources are determined based on data in the design documentation, regulatory and other sources.

- Resource Estimation Method allows to determine with high accuracy the final cost of products for each specific period of time. In this case, all aspects of the upcoming construction, even the additional costs that often arise in construction, are taken into account. The resource method of budgeting is suitable for all stages of the development of design estimates.
- the complexity and volume of the prepared estimate documentation increases many times, which ensures the highest possible accuracy in the calculations;
- thorough work related to the need for a thorough analysis and registration of construction resources and related documentation in the RCSC. The key and most difficult task is to put down price tags for several thousand positions with material resources, both of primary and secondary purpose;
- a full estimate is very difficult to compile, especially when it comes to the design stage, since neither the designers nor the customers have accurate information regarding the cost of each specific resource;
- resource method of budgeting in relation to large objects is possible subject to the availability of specialized computer programs.
The design organization must compile a local resource sheet, with the determination of the consumption of project resources, and only then can we proceed to compile a local resource estimate. If you have a resource sheet, you can calculate the local construction estimate. Often, the estimator is engaged in such work.

Some experts believe that the resource method of preparing estimates is initially limited to objects with a small resource nomenclature. Such methods are especially popular in road construction and the fuel and energy segment.
- Resource-index method for preparing design estimates consists of a resource methodology and indices used for resources used in the construction industry. In fact, we are talking about the use of updated data regarding the cost of a particular type of resource. Relevant information comes from centers specializing in construction pricing.
As for the rest of the resources, the process of transition to the current level of value is carried out through the use of territorial or regional indices.
- Basic index method of preparing estimates for construction and repair measures is based on the use of a whole range of relevant and forecasted indices in relation to the cost determined at the base price level. Rationing according to the level of actual or forecasted prices is carried out by multiplying the base value established in the lines of the estimate and each specific investment and structural element, taking into account regional characteristics.
Determining the cost according to the methodology under consideration, the customer guarantees - the calculated values \u200b\u200bwill not be higher than the regional average. Investors can focus on reasonable and well-defined spending levels.
- Basic compensation method for the preparation of construction estimates - one of the most expensive. It involves the summation of the cost of both work and associated costs. Calculations are carried out at the base price level and associated costs, due to price and tariff adjustments in relation to construction resources (equipment, technical equipment, material and energy resources).

These costs include:
- reimbursement of the cost of intermediary services;
- loss of machine or working time;
- nominal labor productivity;
- overspending of building materials or related material resources.
- Time-based method for preparing estimates involves calculating the cost based on the unit price of time spent by a specialist. The specified methodology is used for local and small-scale works - repair of a domestic nature, local contract.
- Analog method drawing up estimates for the construction of buildings, real estate or other structures is relevant in the presence of a data bank that indicates the prices of already finished or planned for construction objects. The initial data in the case under consideration should coincide completely. According to available data, the analog method is suitable for projects at different stages of readiness, if there is the possibility of using specific fortified indicators and cost values \u200b\u200b(in the case of the area we are talking about 1 square meter, for pipelines - 1 running meter, etc.) .
- A constant or basic price level, which are determined taking into account current prices and norms.
- The forecast level established from the cost of goods and materials in force during the preparation of the estimate documentation.
Estimated documentation is an important element of the project of any construction or system, in connection with which design organizations usually have special departments involved in the development of estimates. In a centralized planning system ex. USSR all calculations of customers with contractors were based on estimates, i.e. estimated cost was the price of construction products. In the market conditions of the Russian Federation, the price of construction products is set on the basis of a mutual agreement between the customer and the contractor on an equal basis in the process of concluding the relevant contract. However, under market conditions, the need for cost estimates remains, although the functions of the estimates vary somewhat. Firstly, the estimated documentation becomes both for the customer and for the contractor a guideline for setting the contract price. Secondly, it is necessary for rational planning and cost analysis for both the customer and the contractor, for intermediate cash settlements between them. When concluding contracts, the estimate documentation is not obligatory, only the protocol of the agreement on the contract price is obligatory. However, the customer has the right to request cost estimates in any form, with any degree of detail. Most customers prefer to use this right in almost all cases, especially when the customer is a government organization. Estimated documentation covering the entire complex of objects under construction is called “consolidated”, since it usually summarizes the documentation for individual objects. If it covers only a specific object or its part (type of work), it is referred to as “object” or “local”, respectively. An estimate document that is calculated without detailed elaboration using aggregated indicators is usually referred to as an estimate. If a detailed calculation of the cost is made according to the working drawings without enlargement, then the resulting document is usually referred to as an “estimate.” Estimated cost is set at each design stage, in connection with which its gradual detailing and refinement is provided. At the pre-design stage, when compiling the “Investment Justification”, the preliminary (estimated) construction cost is determined by order of the investor. It is compiled according to extremely aggregated indicators (per 1 ha of reclaimed land, per 1 m3 of construction volume, per 1 m2 of living space, etc.), because there is no project at this stage yet. In the absence of such indicators, data on the cost of analogous facilities can be used. At the Project stage, enlarged, but more accurate estimates are made. They are based on the drawings of this design stage and include the “Consolidated estimated calculation of the construction cost”, object and local estimated calculations, estimated calculations for certain types of work, including survey and design (compiled before the start of these works), etc. For several types of construction (and, accordingly, several sources of financing) another “Summary of costs” is compiled by type of construction (for example, irrigation and drainage, industrial, housing, etc.).
The basis for the estimated calculations at this stage, as noted, is the project documentation and the current estimated regulatory base of 1991, or prices of 1984. with the introduction of appropriate correction factors. In the absence of estimated standards, individual rates are used, compiled directly for such cases.
In the market conditions of the Russian Federation, four methods of calculating the estimated cost are used: resource resource-index base-index base-compensation
The resource method is a calculation in current (forecast) prices and tariffs of resources (cost elements). With this method, the costs of materials and products, the time spent on operating machines, the labor costs of workers are set separately in physical measurements (m3, ton, piece, person-hour, etc.), and the prices for these resources are taken current (for Estimated time). As a regulatory framework, the Normative Indicators of Material Consumption (NPRM) are used. This method allows in the future to fairly accurately recalculate the estimated cost at new prices. Resource-index method is a combination of a resource method with a system of price indices for resources. Price indices are called the ratio of current prices to base ones. As noted, prices are accepted as base prices at 1.01.91 and it is permissible to use 1984 prices. as amended. The base-index method is the use of a system of current and forecast price indices in relation to the value determined at the base level or the level of the previous period. Unlike the resource-index method, a separate determination of the expenditure of resources in physical terms is usually not done. Reduction to current prices is carried out by multiplying the base cost for each line of the estimate by the corresponding index. The basic compensation method consists in determining the basic cost taking into account the expected changes in prices and tariffs, and during the construction process it is specified depending on the actual changes in these prices and tariffs. The choice of the method of preparation of budget documentation is not regulated by law and is carried out in each case, depending on the terms of the contract (contract) and the general economic situation. The most promising is considered resource and resource-index methods, however, at present, the basic index method prevails in construction. The estimated cost of construction and installation works is divided into three main parts: direct costs; overhead costs; estimated profit (planned savings)
Direct costs include the cost of materials, products, the cost of operating machines and mechanisms, the wages of workers. They are determined on the basis of estimated norms and prices, volumes of structures or types of work, i.e. any of the above calculation methods. Overhead costs reflect the costs associated with the creation of general conditions for construction production, i.e. include the costs of organization, management and maintenance of the construction site. They are most often determined as a percentage of direct costs in accordance with federal norms of overhead costs, or according to individual norms of a particular construction organization. It is also possible to determine them using a system of indicators of overhead costs for types of construction and installation works or aggregated indicators for the main types of construction. Estimated profit (planned savings) is the amount of funds needed to cover costs not directly related to this construction, but necessary for further functioning of the construction organization. This is the cost of paying taxes, the development of production and its infrastructure, material incentives and ensuring favorable living conditions for workers. Estimated profit is usually determined as a percentage of the total cost or labor costs of workers (for example, 50% of labor costs of workers or 12% of the estimated cost of work). The industry-wide standards or individual standards of a particular organization are used for this.
Estimated documentation - the very concept of estimated cost arose even under the planned economy and, in fact, was the equivalent of the construction price, however, one should not think that under the market economy this concept became irrelevant, although the functions of estimated cost have changed, however, the need for it remains, and the role even to some extent increased, this is due to the fact that the estimate documentation is a guideline for setting the contract price for the customer and contractor and in this role is necessary for optimal planning and analysis costs for both sides, as well as for intermediate payments between.
The estimated construction cost is the planned amount of expenses required to create an object in strict accordance with the project. Based on the full estimated cost, capital investments are distributed over the years of construction, sources of financing are determined, and contractual prices for construction products are formed.
It is worth noting that when concluding the contract, the estimate documentation is not mandatory, only the protocol of the agreement on the contract price is obligatory. However, the customer has the right to request estimates in any form, with any degree of detail, and most customers generally enjoy this right in practice, especially if the customer is a government organization.
The basis for the estimated calculations at this stage, as noted, is the project documentation and the current estimated regulatory base of 1991, or prices of 1984. with the introduction of appropriate correction factors. In the absence of estimated standards, individual rates are used, compiled directly for such cases.
The estimated cost of construction consists of the estimated cost of resources and services used in the construction process. The cost of each resource in the total planned estimated cost of construction is determined by the characteristics of two indicators: the amount of demand for a resource at the facility and the current price of this resource:
where: C - the cost of a resource or service in the construction process;
P - the need for a resource to perform all work at the facility;
C is the current price of a resource in the regional market.
The need for any construction resource (labor, machinery, materials, transport, management, services) in planning the cost of construction can be determined in two ways: normative - according to estimated norms and volumes of estimated work and design (resource) - according to drawings, projects, reference materials.
At the stage of “Working Documentation” (RD), object and local estimates are compiled, and SNiP 11.01-95 allows them not to be drawn up if this is not provided for by the contract for the implementation of the RD.
In the market conditions of the Russian Federation, four methods of calculating the estimated cost are used:
Resource
Resource Index
Base index
Basic compensation
The resource method is a calculation in current (forecast) prices and tariffs of resources (cost elements). With this method, the costs of materials and products, the time spent on operating machines, the labor costs of workers are set separately in physical measurements (m3, ton, piece, person-hour, etc.), and the prices for these resources are accepted at the current estimates). As a regulatory framework, the Normative Indicators of Material Consumption (NPRM) are used. This method allows in the future to fairly accurately recalculate the estimated cost at new prices.
Design (resource) method for developing construction estimates
estimate calculation form construction
C \u003d PfrChTsek;
The design method of estimated calculations uses the resource requirements (Ppr) obtained from the design data and the current prices (CTEC) of the regional market for the cost of construction resources.
The planned cost of construction, calculated by the project method, is the most accurate and reasonable calculation of the estimated cost of construction, but it requires highly skilled workers, a permanent monitoring system of regional prices and considerable time for the development of budget documentation. It is advisable to use the design method of estimate calculation at the last stages of determining and agreeing on the construction price, when the information base for estimate calculation has already been collected and verified.
The method is used in the development of executive (detailed) estimates of the contractor with their approval by the customer. In accordance with Art. 709 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, only such budget documentation, as enshrined in the contract, is binding on all participants in the construction project and becomes the regulatory framework in the relations of construction entities in solving problems arising in the course of the project.
Resource-index method is a combination of a resource method with a system of price indices for resources. Price indices are called the ratio of current prices to base ones. As noted, prices are accepted as base prices at 1.01.91 and it is permissible to use 1984 prices. as amended.
The base-index method is the use of a system of current and forecast price indices in relation to the value determined at the base level or the level of the previous period. Unlike the resource-index method, a separate determination of the expenditure of resources in physical terms is usually not done. Reduction to current prices is carried out by multiplying the base cost for each line of the estimate by the corresponding index.
C \u003d PNRCHZbazChITek;
The basic index method of estimate calculation uses the resource requirement (PNR) calculated according to the estimated norms and volumes of estimated work, and the price of resources is taken at basic prices (Tsbaz) with conversion indices (Itek) to the current price level.
A variant of the method is the determination of the cost of construction using basic rates (Rcm) for estimated work.
Rcm \u003d NnrChtsbaz;
Estimated rates are formed as part of the estimated normative bases according to estimated norms of resource consumption (NNR) per unit of estimated work and basic prices (Tsbaz) for resources of estimated norm. Estimated prices are currently developed in the estimated regulatory framework: - EPEP-84; SNiR-91; FER-2001, TEP-2001.
In calculating the estimated cost by the base-index method using estimated prices, the volumes of estimated work (Osm) and the conversion indices (Itek) of the base cost to the current price level are used:
C \u003d PcmHCHmChITek;
The estimated cost of construction, calculated at replaceable prices, is reduced to the current price level using enlarged and approximate indices for types of work, structural elements and objects in general. At the same time, this is the fastest and easiest way to calculate the estimated cost, which does not require highly qualified performers.
The base-index method gives approximate and uncertain results in planning the cost of construction. The method is used in preliminary, rough calculations of the justification of investments, conceptual estimates and in determining the estimated cost at the stages of the pre-contractual competitive selection of construction contractors.
The basic compensation method consists in determining the basic cost taking into account the expected changes in prices and tariffs, and during the construction process it is specified depending on the actual changes in these prices and tariffs.
The choice of the method of preparation of budget documentation is not regulated by law and is carried out in each case, depending on the terms of the contract (contract) and the general economic situation. The most promising is considered resource and resource-index methods, however, at present, the basic index method prevails in construction.
Normative method for the development of construction estimates
C \u003d PNRCHTsek;
The normative method for the development of construction estimates uses indicators of resource requirements (PNR), calculated according to estimated norms and volumes of work, and the price of resources is taken at the current price level (Tstek) according to regional monitoring of the cost of resources.
The estimated normative bases used in the development of budget documentation determine the format of budget estimates: 1984 - Estimated base ESN-84, EPEP-84; 1991 - Estimated base SNiR-91; 2000 - Estimated base of GESN-2001, FER-2001, TER-2001.
The normative method is the most common way of estimated calculations, because its application simplifies the description of construction technology for a limited list of works in the estimated normative bases. The increased uncertainty in the calculation of demand is offset by the maximum possible accuracy in the selection of current prices for resources according to the regional market.
The normative method simplifies the calculation form and reduces the development time of budget documentation. The normative method for the development of construction estimates is used in all automated software products of estimated calculations in construction.
The accuracy and validity of calculating the cost of construction by the normative method is lower than in the design calculation, due to the use of averaged indicators of estimated norms of resource consumption according to a special estimated nomenclature.
The estimated cost of construction and installation works is divided into three main parts:
Direct costs
Overhead
Estimated profit (planned savings)
Direct costs include the cost of materials, products, the cost of operating machines and mechanisms, the wages of workers. They are determined on the basis of estimated norms and prices, volumes of structures or types of work, i.e. any of the above calculation methods.
Overhead costs reflect the costs associated with the creation of general conditions for construction production, i.e. include the costs of organization, management and maintenance of the construction site. They are most often determined as a percentage of direct costs in accordance with federal norms of overhead costs, or according to individual norms of a particular construction organization. It is also possible to determine them using a system of indicators of overhead costs for the types of construction works or aggregated indicators for the main types of construction.
Estimated profit (planned savings) is the amount of funds necessary to cover expenses not directly related to this construction, but necessary for the further functioning of the construction organization. This is the cost of paying taxes, the development of production and its infrastructure, material incentives and ensuring favorable living conditions for workers. Estimated profit is usually determined as a percentage of the total cost or labor costs of workers (for example, 50% of labor costs of workers or 12% of the estimated cost of work). The industry-wide standards or individual standards of a particular organization are used for this.
The estimated cost of individual objects and types of work included in the consolidated estimates for industrial and housing construction is determined by price lists, by estimates for typical and reusable economical and individual projects, tied to local construction conditions, and if they are absent, by estimates, drawn up according to working drawings.
It should be borne in mind that for unique buildings and structures, as well as for objects whose construction will be carried out according to experimental or for the first time applied individual projects using standard design solutions, standard designs and details (for which there are no list prices and cannot the estimates for previously developed projects for similar buildings and structures will be used), the estimated cost is determined by the estimates for the technical project, drawn up, as a rule, according to consolidated estimated standards (CSS ), and only in exceptional cases, in the absence of aggregated estimated norms - at unit prices for construction work, put into force on January 1, 1969, and price tags for installation of equipment, put into effect on January 1, 1972, and for technical work projects - according to estimates drawn up according to working drawings.
The cost of certain types of construction (general construction) special (plumbing, electrical, etc.) and general area (vertical layout of the territory, improvement, etc.) works, as well as certain types of costs (for an organized set of workers, compensation in connection with the removal of land for building and etc.) are calculated according to the estimate of f. No. 3.
The estimated cost of construction and installation work, agreed and adopted by the contractor before the start of construction of the objects, is determined in the consolidated estimate on the basis of object estimates f. No. 2, as well as estimates and estimates for certain types of work and costs (f. No. 3) ", is final and cannot be specified at the stage of development of working drawings, serves as the main document for calculating between the contractor and the customer for the work performed. Estimated cost the equipment necessary for the facilities under construction and the costs associated with its installation are reflected in the budget of f. No. 4 for housing construction.
Since in f. No. 4, the amount of wages for installation work is calculated for each position of the estimate by calculation and is labor-intensive, then from January 1, 1973 a new procedure for determining wages was established. So, when making estimates for electrical work, the amount of wages is determined using coefficients from the estimated cost of these works, calculated at the prices of sections 1-6 and 16-24. The application of these coefficients provides the possibility of linking wages (main and operating machines) to local working conditions. The increase in the estimated cost of electrical work due to increased wages due to difficult local conditions for the performance of work is determined by the following formula: Ds \u003d C x (P-1) x K.
Introduction
Conclusion
List of references
application
Introduction
For the construction of any building and structure, estimates are compiled. The role of estimates in construction is great. Based on the estimated cost, the amount of capital investments is determined, construction financing and calculations for the work performed are carried out. Estimated documentation is used in the process of accounting and reporting, as well as in conducting economic analysis of the activities of construction and installation organizations. Therefore, the correct determination of the estimated cost of construction products is important for the successful implementation of investment and construction activities.
Relevance: This topic is quite relevant today and is of great importance in the construction of any residential buildings.
goal: Calculation of the estimated cost of construction and installation works of a residential building in the 117th quarter of Yakutsk.
Tasks:
1) Preparation of the calculation of local estimates;
2) Preparation of the calculation of object estimates;
3) Preparation of a consolidated estimate of the cost of construction.
Chapter I. The theoretical part.
Estimated construction cost
Estimated cost - the amount of cash necessary for the implementation of the construction in accordance with the design materials.
Estimated cost It is the basis for determining the amount of capital investments, financing of construction, the formation of contract prices for construction products, settlements for completed contract (construction, installation, repair and construction, etc.) work, payment of expenses for the acquisition of equipment and its delivery to construction sites, as well as compensation other costs from the funds provided for by the consolidated estimate.
The basis for determining estimated cost of construction may be the customer's initial data for the development of budget documentation, pre-design and project documentation, including drawings, statements of volumes of construction and installation works, specifications and statements of equipment requirements, decisions on the organization and sequence of construction adopted in the construction organization project (PIC), explanatory notes to design materials, and for additional work - field supervision sheets and certificates for additional work identified during construction and repair tnyh works.
To determine the estimated cost of construction, budget documentation, consisting of local estimates, local estimates, object estimates, object estimates, estimates for certain types of costs, summary estimates of construction costs, cost estimates, etc.
The estimated cost determined by local estimates includes: direct costs, overhead costs and estimated profits.
Estimated Standards
Estimated standards are the generalized name for a set of estimated norms, prices and prices, combined into separate collections. Together with the rules and regulations containing the necessary requirements, they serve as the basis for determining the estimated cost of construction.
Under the estimated norm, we consider the totality of resources (labor costs of construction workers, working hours of construction machines, the need for materials, products and structures, etc.) installed on the adopted measuring instrument for construction, installation or other works.
The main function of the estimated norms is to determine the normative amount of resources, the minimum necessary and sufficient to carry out the corresponding type of work, as the basis for the subsequent transition to cost indicators.
Estimated standards are divided into the following types:
1. state estimated standards - GOS;
2. industry estimated standards - OCH;
3. territorial estimated standards - TSN;
4. company estimated standards - FSN;
5. individual estimated standards - ISN.
State Estimated Norms (GOS) - these are the initial estimated standards designed to determine resource requirements: labor costs of workers, construction machines, materials, when performing a full range of basic, auxiliary and related construction and installation works.
Sectoral estimated standards (OST) are the estimated standards introduced for construction carried out within the relevant industry (energy, transport, water management, mining, gas pipelines, communications, certain types of industrial facilities, etc.).
Territorial building codes (TSN) are collections of territorial building codes that determine the technical, organizational and economic aspects of design and construction in the territories of various constituent entities of the Russian Federation.
company estimated standards (FSN) - these are estimated standards that take into account the real conditions of activity of a particular organization - the manufacturer of the work. As a rule, this regulatory framework is based on standards of the state, industry or territorial level, taking into account the specialization of the contractor
individual estimated standards (ISN). In the absence of estimated norms and prices of separate standards in the current collections on the work technologies provided for in the project, it is allowed to develop the corresponding individual estimated norms and unit prices, which are approved by the customer (investor) as part of the project (working draft). Individual estimated rates and prices are developed taking into account the specific conditions of the work with all the complicating factors.
The use of company and individual estimated standards for determining the cost of construction, the financing of which is carried out with the involvement of the federal budget, is recommended after their approval by the appropriate authorized federal executive body in the field of construction.
When applying individual estimated norms and prices, accrual of increasing coefficients on them is not performed.
Estimated standards are divided into elemental and enlarged.
Elemental estimated standards include state elemental estimated norms (GESN-2001) and individual elemental estimated norms, as well as norms for types of work.
The aggregated estimated standards include:
· Estimated standards, expressed as a percentage, including:
· Standards of overhead costs;
· Standards of estimated profit;
· Estimated norms of additional costs in the production of construction works in the winter;
· Estimated cost standards for the construction of temporary buildings and structures;
· Indices of changes in the cost of construction, installation and design and survey work, set to a base price level;
· Cost standards for the maintenance of the customer (technical supervision)
· Aggregated estimated standards and indicators, including:
· Aggregated indicators of the basic cost of construction (UPS);
· Aggregated indicators of the base cost by type of work (UPSB BP);
· Collections of indicators of cost for types of work (collections of TAC);
· Aggregated resource standards (URN) and enlarged resource indicators (UPR) for certain types of construction;
· Aggregated indicators of estimated cost (OSS);
· Price lists for the consumer unit of construction products (PPE);
· Price lists for the construction of buildings and structures;
· Estimated cost standards for equipment and inventory of public and administrative buildings (NIAZ);
· Estimated rates of costs for tools and equipment of industrial buildings (NIPZ);
· Indicators on the objects of analogues;
· And other regulations.
Methods for determining the estimated cost of construction
When making estimates (calculations), the following methods for determining the estimated cost can be used:
Basic index;
Resource
Resource Index;
1. The base-index (index) method of determining value.
In this case, the cost of work is determined on the basis of data taken from unit rates and indicators of conversion indices to current prices (published every month). Thus, the base-index method for determining the estimated cost makes it possible to obtain the most relevant cost indicators in relation to the date of the estimate. There are several methods for using allocation indices (KPs) in budgeting:
In general, the estimate. In this case, the amount of direct costs is multiplied by KP. This method is applicable for making estimates for one type of work, materials and other resources.
For each section of the estimate. In the event that the budget includes several sections (installation of electrical systems, equipment repair, etc.), then the corresponding index of conversion to current prices is applied to a certain type of work.
To each separate rate.
To the elements of prices (elements of direct costs). Allocation indices are applied to each item from the quotation with their subsequent summation, to determine the final direct costs.
PZ \u003d (RFP (units) * KPkZP + EM (units) * KPkEM + Mat (units) * KPkMat) * Volume
ZP (unit) - Wages of workers at a unit rate
KPKZP - Salary conversion index
EM (unit) - The cost of operating machines at a unit price
Kpkem - Recalculation index for the operation of machines
Mat (units) - The cost of materials at a unit price
Cpkmat - Conversion index to materials
Volume - the amount of work at a rate.
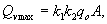

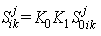







Learning environment: new projects A typical project of a school with 825 seats
A catalog of typical projects of social infrastructure buildings has been created in Moscow Region
A catalog of typical projects of social infrastructure buildings has been created in Moscow Region
Turnkey Cottage Construction Roadmap
The report of the head of the Ministry of Construction of Russia Mikhail I at a meeting of the Commission under the President of the Russian Federation on monitoring the achievement of targets of socio-economic development of the Russian Federation