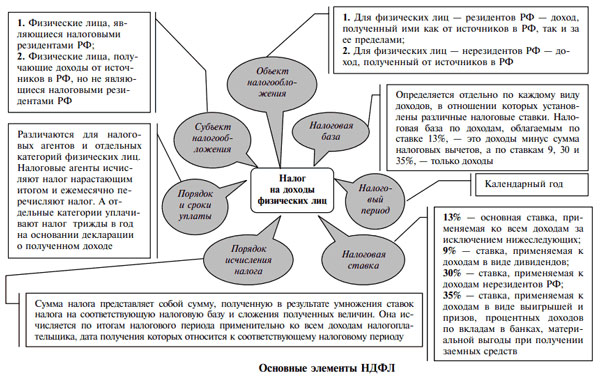
In the Russian Federation, individuals who receive certain types of income are required to pay tax on them. All of them are classified into categories for residents of the Russian Federation and foreign persons, as well as for ordinary citizens and individual entrepreneurs. The last category includes individuals in private practice.
The civil service of a citizen on the territory of a foreign state is not a basis for recognizing him as a non-resident. Residents of the Russian Federation include Russian civil and military employees. Their income is also subject to income tax.
Income tax is calculated and transferred by both the taxpayers themselves and their tax agents. It depends on the type of income received. Personal income tax reporting must be submitted directly by the persons making the transfer. Therefore, it is important to know who pays personal income tax and in what terms.
Income tax must be paid by various categories of individuals. Depending on who pays personal income tax, the terms for transferring tax to the budget also differ. All taxpayers must report no later than April 15 of the year following the reporting year (clause 1, article 229 of the Tax Code). For example, the deadline for filing a declaration for 2019 is April 30, 2019.
The table shows the categories of personal income tax payers and the timing of their payment of tax:
For non-fulfillment or faulty fulfillment of the obligations of income tax payers, the law provides for liability:
| Payer category | Penalties | ||
| Late transfer of personal income tax | Late submission of the report (Article 75 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) | ||
| Up to 10 working days (clause 1, article 119 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) | More than 10 working days (clause 1 clause 3, clause 11 article 76 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) | ||
| Ordinary individuals | 5% of the tax amount for each missed month. Not less than 1000 rubles. and not more than 30% of the tax payable. | Daily penalties | |
| IP | Suspension of operations on bank accounts | ||
Accountable income
In accordance with Article 41 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, income is an economic benefit received by a citizen in the form of money or a natural product, if it can be assessed and determined in accordance with the rules of Chapter 23 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Russians and foreigners receiving income are required to pay taxes on them. The former pay personal income tax on all income, regardless of what source they receive: Russian or foreign. The second - only from income received from Russian sources.
The list of income subject to personal income tax is presented in Article 208 of the Tax Code. Moreover, it is open, which means that they include any types of income that are not classified by law as non-taxable income tax. These include income from rent, property sales, insurance payments, dividends, interest, remuneration for services or work, etc.
The list of income that is not subject to personal income tax is established by Article 217 of the Tax Code. It is closed and includes income such as unemployment benefits, pensions, alimony.
Important Process Notes
Submission nuances
There are two options for calculating and paying personal income tax to the budget: by an individual independently or by his tax agent.
The second case refers to the work of citizens in enterprises for a salary, from which the employer is obliged to calculate income tax himself and transfer it to the budget. At the same time, income includes not only direct wages, but also other remuneration, including sick leave. For the withheld and paid amounts, tax agents must report to the Federal Tax Service.
It is necessary for citizens who receive income in other cases to independently calculate and pay tax:
- from actions with property;
- from foreign sources;
- from lottery winnings, etc.
To report to the state on income received, it is necessary to fill out a declaration in a strictly prescribed form () and submit it to the tax service within the time limits established by law. You need to report before April 30 of the year following the year of receipt of income, and pay taxes - until July 15.
Allocation scheme from dividends
Enterprises must report to the tax service on the dividends paid and the amounts of income tax withheld from them with certificates and.
Dividends of Russian citizens are subject to personal income tax at a rate of 13% if they have been paid since 2019.
Deductions are not included in the calculation. The tax is calculated not on an accrual basis, but on each payment made. The calculation is affected by the receipt by the enterprise of dividends from other legal entities.
If not, the formula is used:
personal income tax \u003d Dividends x 13%
If the organization receives dividends from other companies, the calculation procedure is as follows. First, the personal income tax deduction is determined by dividing the accrued dividends of a particular participant by the total amount of accrued dividends of all participants and multiplying by the amounts received.
Who pays tax and how much
The Tax Code establishes five different income tax rates, depending on the category of taxpayers and the types of income received:
| 9% | Minimum bid. Established for the taxation of dividends, interest on mortgage certificates and bonds issued before 2007. |
| 13% | The most common rate. Most of the income of Russian citizens is taxed on it. |
| 15% | Provided for income in the form of dividends received by Russian citizens from organizations that are not tax agents (introduced in 2008). |
| 30% | Income of foreigners received from Russian sources is taxed, except for equity participation in the company (15%). |
| 35% | Max bet. It is taxed on winnings, interest income, prizes, etc. Since 2008, in certain cases, interest income on fixed-term pension deposits in banking institutions. |
Specific points in the requirements
Dismissing an employee
The features of paying personal income tax upon dismissal of an employee are explained by the Tax Code and the Ministry of Finance in letter No. 03-04-06 / 4831 of 2013.
The date of receipt of income from the employer in the form of earnings is the last day of the working month for which payments are accrued. If an employee is dismissed within a month, the last working day becomes such a date (clause 2, article 223 of the Tax Code).
The tax agent is obliged to transfer income tax on the day of payment of income or the next day in the case of settlement with the employee through the cash desk of the enterprise (clause 6 of article 226 of the Tax Code). The Ministry of Finance explained that these terms should be guided in the case of the last settlement with the employee.
From the foregoing, it follows that when paying wages to a dismissed specialist, the personal income tax card must be transferred on the same day. In the case of remuneration from the organization's cash desk, the payment of tax on the next day is allowed.
Relationship between employee and employer
Income tax on earnings received at the enterprise is calculated and paid for by the employer. However, he only carries out these operations and reports on them to the state. The tax burden falls on the employees themselves, i.e. 13% of income is deducted from their salary.
To the question of who actually pays personal income tax, the employee or the employer, the answer is clear. The latter is a tax agent that pays personal income tax instead of employees, but at their expense.
Details when selling an apartment
When selling personal expensive property, such as an apartment, house, land, a citizen receives income subject to personal income tax. Therefore, it is his responsibility to independently calculate the tax and pay it to the budget. You must report your actions to the tax office.
However, the sale of not all property is subject to taxation. It is necessary to pay to the budget 13% of the income received from the sale of property that has been owned by the owner for less than 5 years. It doesn't matter if he used it or not. The time of ownership starts counting from the receipt of the certificate of registration.
Tax legislation provides for the possibility of reducing the tax burden when selling an apartment. So, the amount of tax can be reduced by using the right to a property deduction. This opportunity is convenient when buying another residential property in the same year in which the first one was sold.
It is important to know that the use of the property deduction is possible only for working citizens and only once in a lifetime.
The second way to reduce the tax when an apartment is sold is to take into account the costs incurred by the seller when buying the sold object.
Example: an apartment owned by a citizen for 2 years was sold to him for 2.5 million rubles. He bought it for 1.8 million rubles. As a general rule, the tax amount will be 325,000 rubles (2,500,000 x 13%). It is possible to reduce the tax base at the expense of the costs of buying this apartment, i.e. by 1.8 million rubles. Therefore, the tax will be (2,500,000 - 1,800,000) x 13% = 91,000 (rubles).
To use this opportunity, the payment made for an apartment must have official confirmation: a contract of sale reflecting the cost of housing.
Loans and leases
It is necessary to pay income tax under a loan agreement only if there is a profit from it, which the recipient can dispose of. This rule follows from the provisions of Articles 41 and 210 of the RF Tax Code. Such a loan is taxed at the normal rate of 13%.
When obtaining an interest-free loan, the borrower does not receive economic benefits. Therefore, there is nothing to tax personal income tax. But, if such a loan is received from a legal entity, then the borrower benefits in the form of savings on interest on a bank loan. According to tax legislation, it is a direct income - a material benefit, and is subject to personal income tax.
If a legal entity leases premises from a citizen, it becomes a tax agent. Therefore, the company has an obligation to calculate, withhold and pay income tax on rent to the budget (clause 2 of article 226 and article 228 of the Tax Code). It is impossible to shift this obligation to the lessor even under the terms of the contract.
The tax is calculated according to the usual rules at a rate of 13% (landlord - a citizen of the Russian Federation) or 30% (landlord - a foreigner) from the amount of rent. It is necessary to carry out the tax calculation at the time of each payment. In fact, you need to transfer the amount to the landlord minus personal income tax.
Insurance and service agreement
From the remuneration of contractors - individuals who are not individual entrepreneurs, the enterprise must withhold and pay personal income tax. In addition, they pay insurance premiums to the Pension Fund and the Federal Migration Service. Payments to the FSS, when valid, are not taxed.
The company pays insurance premiums for compulsory insurance against accidents at the enterprise and the receipt of occupational diseases, if it is provided for under the service agreement.
The remuneration of a citizen received under an agency agreement is subject to income tax at the rates of 13% and 30% for residents of the Russian Federation and non-residents, respectively.









Transfer of losses to the future in 1C: Accounting 8
Sample certificate of no debt
Issuance of money for a business trip in cash and on a card
payroll taxes
Preferential pension: who is entitled, how to get