- double warehouse receipt;
- warehouse receipt as part of a double certificate;
- certificate of pledge (warrant) as part of a double certificate;
- simple warehouse receipt.
The fifteenth type of Russian security is one that has received citizenship rights in accordance with the Law of the Russian Federation “On Mortgage (Pledge of Real Estate),” which came into force on July 16, 1998. The last of the securities available in Russia is investment share(in accordance with the Law of the Russian Federation “On Investment Funds”, 2001).
Government bond and just a bond- this is the same type of security with the only difference, consisting in the fact that government bond can only be released by the state, but simply a bond - any legal entity.
If a bond is issued by the government, then such a bond is called a government bond. If local governments - then municipal. Legal entities also issue bonds: banks - bank bonds, other companies - corporate ones. Individuals do not issue bonds.
Banking savings book to bearer in fact there is a type of bank certificate(along with certificates of deposit and savings certificates).
Privatization check ended its existence by 1996.
The following eight are legally (legally) permitted for release and circulation in Russia: economic types securities: shares, bonds, bills of exchange, checks, bank certificates, bills of lading, mortgages and investment shares.
Promotion
Promotion - in accordance with the law of the Russian Federation “On” is “an emission security that secures the rights of its owner (shareholder) to receive a portion of the profit joint stock company in the form of dividends, participation in the management of the joint-stock company and part of the property remaining after its liquidation.”
Economic definition is a security that certifies a single contribution to the authorized capital of a business partnership with the ensuing rights for its owner.
Bond
Bond- in accordance with the law of the Russian Federation “On the Securities Market” - this is “an issue-grade security that secures the right of its holder to receive from the issuer of a bond within the period specified by it the nominal value and the percentage of this value or property equivalent fixed in it”;
Economic definition is a security that certifies a single debt obligation of the issuer (state or any other legal entity) for the return of its nominal value after a certain period in the future on terms that suit its holder.
Bill of exchange
Bill of exchange- a security certifying a written monetary obligation of the debtor to repay the debt, the form and circulation of which are regulated special legislation— bill law;
- promissory note- this is a security certifying the unconditional obligation (promise) of the debtor to pay the amount of money specified in it to the holder of the bill after a certain period of time;
- bill of exchange- this is a security that certifies an offer to the debtor to pay the amount of money indicated in it to the person designated in it after a certain period.
Check
Check- a security document certifying a written order from the drawer of the check to the bank to pay the recipient of the check the amount of money specified in it during the period of its validity. A check is a type of bill of exchange that is issued only by a bank.
Bank certificate
Bank certificate- a security that is a freely negotiable certificate of a monetary deposit (deposit for legal entities, savings for individuals) in a bank with the latter’s obligation to return this deposit and interest on it after a specified period in the future.
Bill of lading
Bill of lading - a security, which is a document of a standard form, accepted in international practice, for the transportation of cargo, certifying its loading, transportation and right to receive it.
Mortgage
Mortgage - this is a registered security certifying the rights of its owner in accordance with a mortgage agreement (real estate pledge) to receive monetary obligation or the property specified therein.
Investment share
Investment share- a registered security certifying its owner’s share in the ownership of the property constituting a mutual investment fund.
The listed types of securities typical for countries with highly developed market economy, are not exhausted, and therefore we can predict that in the future the number of types of securities permitted by Russian legislation will increase.
Russian securities can be distributed according to the main listed characteristics as follows.
Comparative characteristics (classification) of Russian securitiesExcept listed types securities that can be called basic, or primary, securities, in world practice there are securities that are based on primary ones, and therefore are considered derivatives in relation to them. Derivatives, or secondary securities, include securities based on stocks and bonds: depositary receipts, stock warrants, etc.
Secondary or derivative security is a security that provides its owner not directly with any property rights, but with rights to any underlying securities and, through them, to property rights.
Depository receipt - this is a security indicating ownership of a certain number of shares of a foreign issuer, but issued for circulation in the investor’s country; This is a form of indirect purchase of shares of a foreign issuer.
Stock warrant- this is a security that gives its owner the right to buy from a given issuer a certain number of its shares (bonds) at a price set by him during a period of time specified by him.
Characteristics of the security
The form has a whole series details, or economic characteristics, along with their essential (“capital”) content. Specified market characteristics usually have a pairwise opposite nature (for example, paper or paperless forms of existence of a security), and therefore securities are classified depending on which feature of the corresponding pair they meet. The totality of these features inherent in a security constitutes it economic content.
The set of characteristics that any security has includes:
Timing characteristics:- period of existence: when it was released into circulation, for what period of time or indefinitely;
- form of existence: paper, or, legally speaking, documentary form, or paperless, undocumented form;
- nationality: a security of domestic or another state, i.e. foreign;
- procedure for registering the owner: to bearer or to a specific person (legal, individual);
- form of issue: emission, i.e. issued in separate series, within which all securities are exactly the same in their characteristics, or non-emission (individual);
- type of issuer, i.e. the one who issues a security to the market: state, corporations, individuals;
- degree of negotiability: freely circulated on the market or there are restrictions;
- risk level: high, low, etc.;
- availability of accrued income: whether some income is paid or not;
- transfer procedure (form of address): delivery, assignment of rights of claim: assignment or endorsement;
- Registration: registered or unregistered;
- type of denomination: constant or variable.
Classification and types of securities
Depending on various characteristics, securities are classified as follows:
Types of securities by duration:
- urgent (lifetime is limited in time);
- perpetual (lifespan is not limited in time);
Securities, issued for the entire life of the person obligated under them, are not directly related to any time period, and therefore they are perpetual securities. These usually include shares. Securities issued for a limited period of time, regardless of whether it is specified when the security is issued or will be determined during its circulation, constitute a group of futures securities.
Future securities have a lifetime established upon their issue or a procedure for establishing this period. Typically, fixed-term securities are divided into three subtypes:
- short-term, with a maturity of up to 1 year;
- medium-term, having a maturity from 1 year to 5 years;
- long-term, having a maturity from 5 to 30 years (mortgage securities, by law, can be issued with a maturity of up to 40 years).
Fixed-term securities, the circulation period of which is not regulated in any way, i.e. they exist until the moment of redemption, the date of which is not indicated in any way when the security is issued, but only the procedure for their cancellation (redemption) is established, are called revocable.
Types of securities by form of existence:
- paper or documentary;
- paperless, or undocumented;
The classic form of existence of a security is paper form, in which the security exists in the form of a document. The development of the securities market requires the transition of many types of securities, primarily equity ones, to a non-documentary form of existence.
Types of securities by nationality:
- national (Russian);
- foreign;
Types of securities by form of ownership:
- bearer, or bearer securities;
- registered, which contain the name of its owner and are registered in the register of owners of this security;
Ownership of a security can be registered or bearer. A bearer security does not record the name of its owner, and its circulation is carried out by simple transfer from one person to another. A registered security contains the name of its owner and, in addition, is registered in a special register. It is usually transferred by agreement of the parties or by assignment.
If a registered security is transferred to another person by making a transfer note (endorsement) on it, or by order of its owner, then it is called an order security.
Types of securities by form of issue:
- emission, i.e. issued in large quantities, within which all securities are absolutely identical;
- non-emissive, usually produced individually or in small batches without state registration;
The issue of securities may or may not be accompanied by their mandatory registration with the authorities public administration. Typically, equity securities are subject to state registration, since their issue affects the interests of a large number of market participants. According to Russian legislation, issued shares, bonds, bank certificates(registered Central Bank) and mortgages. Other types of Russian securities, regardless of the size of their issue, are not subject to state registration.
Issue-grade securities are usually issued in large series, which are subject to state registration. These are usually stocks and bonds. Non-issue securities are issued without any state registration.
Types of securities by type of issuer:
- government securities are usually various types bonds issued by the state;
- non-state, or corporate, are securities that are issued for circulation by corporations (companies, banks, organizations) and even individuals.
Government securities- securities issued by . They occupy a special place among securities.
The state is not a capitalist and does not use funds raised through securities to generate income; it only redistributes them through or through its financial system, i.e. acts as an intermediary. Consequently, government securities are not a representative of directly functioning capital, but a representative of capital that the state does not have, which returns to the economy in a roundabout way (through the salaries of civil servants, the military, the purchase of goods, for example, military equipment, etc.). Therefore, government securities are an indirect representative of real capital.
Types of securities by risk level:
- low risk;
- medium risk;
- high-risk;
According to the level of risk, securities are conventionally divided into risk-free and risky. Risk-free- these are securities for which there is practically no risk. In world practice, these are short-term (1-3 months) government debt obligations (treasury bills). All other securities according to the level of risk are usually divided into low risk e (these are usually government papers), medium risk(this is usually corporate bonds) And high-risk(these are usually shares). There are also higher-risk market instruments than ordinary stocks and bonds.
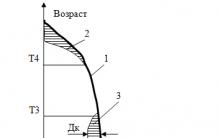
Graphically, the place of the main types of income-generating securities from the point of view of the ratio of risk and level of profitability is usually depicted as follows (Fig. 2.3).
In turn, each type of basic securities is divided into subtypes, etc.

Types of securities by degree of negotiability:
- market, or freely circulating;
- non-marketable, which are issued by the issuer and can only be returned to him; cannot be resold;
The main types of securities are marketable, i.e. they can be freely sold and bought on the market. However, in a number of cases, the circulation of securities may be limited, and the security cannot be sold to anyone other than the one who issued it, and then after a specified period. Such securities are called non-marketable.
Types of securities according to the form of raising capital:
- equity, or ownership, which reflect a share in authorized capital society;
- debt, which is a form of capital borrowing ( cash).
Types of securities by type of par value:
- with a constant denomination;
- with variable denomination;
According to Russian legislation, each security has its own denomination or face value. However, in world practice it is allowed to issue, for example, shares without a monetary par value, or with a zero par value. In this case, it is indicated what share in the authorized capital is one share, and therefore its par value, calculated by dividing authorized capital by the number of shares, changes each time the size of this capital changes, and does not remain unchanged as in the case when the par value of the security is set at the time of its issue. If a security is issued with a monetary denomination, then it is constant denomination paper. If a security is issued without a monetary face value (zero face value), then it is variable denomination paper.
Types of securities according to the form of capital servicing:
- Investment (capital) securities are an object for investing money as capital, i.e., for the purpose of generating income.
- Non-investment securities serve monetary settlements in commodity or other markets. Typically, this role is played by bills of lading, warehouse receipts, and bills of exchange.
Types of securities based on the availability of accrued income:
- no income;
- with accrued income;
From the point of view of accruable income, securities, as a rule, are profitable, but they can also be non-income when for their owner they are a simple certificate of goods or money, and not capital. Income on a security can be accrued in the form of a dividend (shares), interest (debt securities) or a discount, i.e., the difference between the par value of the security and its lower purchase price.
A security is a document certifying, in compliance with the established form and (or) mandatory details, property rights, the exercise or transfer of which is possible only upon presentation. With the transfer of a security, all rights certified by it are transferred in the aggregate.
Civil Code of the Republic of Belarus in Art. 144 lists the main types of securities, but does not pay special attention to their classification, which is not only scientific, but also practical significance and application.
Securities in educational and scientific literature are classified on the following grounds (criteria):
1) by release method they are divided into:
Emission (issued in series that have an individual scope of rights);
Non-emission (produced individually and have an individual scope of rights).
2) according to the method of designating an authorized person:
Registered (issued in the name of a specific person with the right of transfer in the order cessions);
Warrants (issued in the name of a specific person, but with the right to transfer to other persons by way of endorsement);
Bearer (without indicating a specific copyright holder).
3) by type of person (issuer) issuing the securities:
Government securities (issuer - state and municipal entities);
Private (issuer - legal entities and individuals).
Cash (to receive a certain amount of money - checks, bills, bonds);
Commodity (for receiving a certain amount of goods - bills of lading, warehouse receipts);
Corporate (including participation in the management of joint stock companies - common shares).
A security should also be distinguished from other documents. Its main difference is that it must have a strictly defined form and the presence of mandatory details. Otherwise, the security will be void (see: Article 145 of the Civil Code).
The transfer of rights under a security is carried out in accordance with Art. 147 Civil Code.
1) Rights under a bearer security are transferred by simply transferring it to another person. Therefore, it has a high turnover capacity and a very low degree of protection from attacks by third parties.
2) The transfer of rights under a registered security occurs in the order cessions(assignment of demands). Assignor (transmitting document) answers to assignee (accepting a security) for the validity of the requirements, but not for his (her) fulfillment by the debtor.
3) Rights under an order security are transferred by making an endorsement on this document - endorsement. Endorser (who transferred the security) is responsible to endorser not only for the validity of the requirements, but also for their fulfillment by the debtor. An endorsement can be a blank endorsement (without indicating the person to whom the execution should be made) or an order (indicating the person to whom or on whose order the execution should be made).
An endorsement may be limited only to an instruction to exercise the rights certified by a security, without transferring these rights to the endorsee (authentic endorsement). In this case, the endorsee acts as a representative.

Types of securities
1) Promotion- a security certifying the right of its holder ( shareholder) to participate in the management of the affairs of the joint-stock company (simple share), to receive part of the profit in the form of dividends and part of the property upon liquidation of the joint-stock company.
The issuer is JSC. Shares can only be registered.
2) Bond- this is a security that certifies the right of its holder to receive from the issuer within a specified period of time a sum of money in the amount of its face value, as well as the interest fixed in it, or other property rights (for example, a scarce product).
Bonds can be issued by the state or private individuals (JSC), and be registered or bearer.
3) Bill of exchange- a security certifying the unconditional obligation of the drawer (the person specified by him) to pay a certain amount to the holder of the bill upon the arrival of the period specified in the bill.
Bills of exchange are of two types: simple and transferable.
Promissory note represents an unconditional obligation of the drawer to pay the holder of the bill, or another person specified by him, a certain amount within a specified period.
Bill of exchange is a security containing an unconditional offer by the drawer to the person for whom the bill is issued to pay a certain amount of money to the bearer of the bill, or to another person specified by him, within a specified period upon presentation. In other words, in a bill of exchange the payer is not only the drawer, but also another person.
4) Check- a security containing an unconditional written order from the drawer to the payer (bank) to pay the holder of the check the amount specified in it. Checks can be personal or transferable. A personal check is not transferred, but a transferable check is transferred according to the rule of order securities.
5) Deposit or savings certificates- these are securities that certify the right of the investor (individual or legal entity) to receive upon expiration deadline deposit amounts and interest. Early termination certificate leads to loss of interest.
Certificates can be personal and bearer, urgent or on demand.
6) Bill of lading- a valuable commodity paper certifying the right of its holder to receive the cargo specified in it from the carrier.
A bill of lading can be registered, order or bearer.
7) Warehouse receipt- a valuable commodity paper certifying the right of its holder to receive the goods specified in it from the warehouse.
The Civil Code of the Russian Federation provides a legal definition securities as a document of the established form and details, certifying property rights, the implementation or transfer of which is possible only upon its presentation. This definition reflects a certain set of economic relations that arise in the process of circulation of securities.
In market conditions, its participants enter into numerous relationships with each other, including regarding the transfer of money and goods. These relationships are fixed, formalized and consolidated in a certain way. In this sense, a security is a form of fixation of economic relations between market participants, which itself is the object of these relations. The conclusion of any transaction or agreement consists of the transfer or sale of a security in exchange for money or goods. But a security is not money or a material commodity. Its value lies in the rights it gives to its owner. The latter exchanges goods or money for a security only if he is sure that this paper is no worse than the money or goods themselves. Since money and goods are different shapes existence of capital, then the economic content of the security can be expressed as follows.
Security - this is a special form of existence of capital that replaces it real shapes, expresses property relations, can independently circulate on the market as a product and generate income.
This form of capital functions alongside the monetary, productive and commodity forms. The owner of the security does not have real capital, but has all the rights to it, which are fixed by the security. It makes it possible to separate ownership of capital from capital itself and, accordingly, to include the latter in the market process in such forms as are necessary for the economy itself.
The concept of a security is multifaceted, since economic relations, which are expressed by it, are very complex and are constantly changing and developing. All this finds expression in new forms of existence of securities. In this regard, it is often difficult to give a strictly scientific legal definition of a security in all cases. Therefore, Russian legislation may provide a list of specific types of securities recognized by the state that are available in practice.
Properties of securities. A security has a number of properties:
- * redistributes funds between industries and areas of the economy; territories and countries; groups and segments of the population; economic entities and the state, etc.;
- * provides certain additional rights to its owners in addition to the right to capital. For example, the right to participate in management, to receive information, to have priority in certain situations, etc.;
- * provides income on capital and (or) return of capital itself.
A security has a number of properties that make it similar to money. The main property is possibility of exchange for money in various forms (by redemption, purchase and sale, return to the issuer, assignment, etc.). It can be used in calculations, be the subject of a pledge, be stored for a number of years or indefinitely, be inherited, serve as a gift and participate in other acts of civil circulation.
Initially, all securities were issued only in documentary form, i.e. in the form of special paper forms, which is where their name comes from. However, the development of market relations in recent decades has led to the emergence new form existence of a security - undocumented. This transition is due to the fact that the number of circulating securities, primarily shares and bonds, is increasing;
- * many rights that are assigned to the owners of a security can be exercised regardless of its form. For example, payment of income on a security, purchase and sale of a security can be carried out without its availability as material carrier these rights;
- * the book-entry form of a security can speed up, simplify and reduce the cost of its circulation in terms of settlements, transfer from one owner to another, storage, accounting and taxation;
- * this form is closely related to structural changes in the securities market (in particular, with an increase in the number of registered securities and a decrease in the share of bearer securities).
Classification of securities. There are registered, bearer and order securities.
In a registered security, the name of the owner is recorded on its form and (or) in the register of owners. IN bearer In a security, the name of the owner is not recorded directly on it, and its circulation does not require any registration. The rights under an order security belong to the person named in it, who exercises these rights or appoints another authorized person by his disposal.
From the point of view of market participants, a bearer security has significant advantages over a registered one, since the process of transferring rights to capital is accomplished immediately by transferring the security from its owner to the buyer. Apart from the costs of redemption of such a security, its circulation requires almost no other expenses from market participants. In this sense, at the first stage of market development, the issue of bearer securities in documentary form is the fastest, cheapest and easiest way to form a market.
A registered security, unlike a bearer security, has two important properties. Firstly, its owner is always known, and secondly, due to the fact that all transactions with this paper are subject to registration, these transactions become available for control and taxation by the state. Therefore in developed market there is a tendency to increase the issue of registered securities, since, on the one hand, issuers are interested in this, since this allows them to control all transfers of property rights, and on the other hand, the state, since it is expanding its tax base.
Depending on forms of property relations, expressed by a security, a distinction is made between equity and debt securities. Share a security confirms the ownership relationship of its owner to part of the issuer's property. Debt a security expresses a loan relationship between its owner and the issuer, who undertakes to repurchase it within a specified period and pay a certain interest.
In modern world practice, there are two large classes of securities: basic and derivatives.
Basic securities are based on property rights to any asset: goods, money, property, etc. They are based on any assets, which do not include the securities themselves (stocks, bonds, bills, mortgages, etc.). Derivatives are issued on the basis of the underlying securities (warrants, depository receipts, etc.) or in connection with changes in the price of the exchange asset underlying this security (futures contracts, options, etc.).
Signs of securities. Each type of securities represents a certain set of them, for which all the characteristics inherent in the securities are common.
A security has a certain set of characteristics:
- * the period of existence of a security - the time of issue for circulation, for what period of circulation or indefinitely;
- * form of existence - documentary or non-documentary;
- * nationality - domestic or foreign security;
- * territorial affiliation - in which region of the country this security was issued;
- * the type of asset underlying the security, or its original basis (commodities, money, total assets and others);
- * ownership order - a security to bearer or to a specific person (legal entity, individual);
- * release form - emission, i.e. issued in separate series, within which all securities are exactly the same in their characteristics, or non-issue (individual);
- * form of ownership and type of element;
- * nature of negotiability - freely circulates on the market or there are restrictions;
- * economic entity in terms of the type of rights that the security provides;
- * degree of risk - high, low, etc.;
- * availability of income - whether some income is paid on the security or not;
- * form of investment - investing money in debt or to acquire property rights.
Main types of securities.
1. One of the main types of securities is shares. The purpose of the stock market is to bring together savings and relatively small capital to form a large money capital and financing of profit-generating production. A share expresses the relationship of ownership, co-ownership of an enterprise in joint stock form. Income from shares is paid in the form of a dividend, which the shareholder can receive from part of the net profit current year joint-stock company, distributed among shareholders in the form of a certain share of their nominal value.
Promotion - This is an issue-grade security that secures the holder’s rights to receive part of the profit of the joint-stock company in the form of dividends, to participate in management and to part of the property remaining after its liquidation.
Based on the form of income assignment, a distinction is made between ordinary and preferred shares.
Ordinary share gives the holder the right to a share in the authorized capital of the company, to participate in the management of the company by voting when making decisions general meeting shareholders to receive a share of profits from the company's activities after payment to holders preferred shares.
Preferred shares give the holder an advantage over the holder of ordinary shares in the distribution of dividends and property of the company in the event of its liquidation. Preferred shares differ from ordinary shares in that their dividend is usually set at fixed rate. Dividends on preferred shares are usually paid before dividends are paid on ordinary shares; holders of preferred shares have a preferential right to a certain share of the company’s assets upon its liquidation; holders of preferred shares, as a rule, do not have preemptive rights to purchase shares of a new issue and voting rights. These shares carry voting rights only if dividends have not been declared a certain number of times.
- 2. Bond - a security certifying the deposit by its owner of funds and confirming the obligation to reimburse him the nominal value of this security within the specified period, with payment of a fixed percentage (unless otherwise provided by the terms of issue). Bonds of all types can be distributed among enterprises and citizens only on a voluntary basis. The fundamental difference between a bond and a stock is that the owners of bonds, unlike the owners of shares, are not co-owners of the joint stock company, but its creditors. It is believed that this circumstance generally reduces the riskiness of this type of investment, since the bond holder has the right of priority in receiving income or returning his fixed assets in the event of a decrease in the profit of the enterprise, its insufficiency to satisfy all legal claims of creditors and co-owners, and also in case of bankruptcy.
- 3. Important security - bill of exchange Currently financial markets operate with two main types of bills: simple and transferable.
- * Promissory note (solo bill) is an unconditional debt obligation of the established form, expressing the obligation (of the drawer) to pay a certain amount of money to the creditor (the holder of the bill) at a certain time and in a certain place. A promissory note is issued by the borrower.
- * Bill of exchange (draft) is a written order from the drawer (drawee) to the drawee (payer) to pay the latter a certain amount of money to a third party.
- 4. Another type of securities - deposit and savings certificates - a written certificate of the issuing bank on the deposit of funds, certifying the right of the depositor (beneficiary) or his successor to receive, upon expiration of the established period, the amount of the deposit (deposit) and interest on it. Issuers of deposit and savings certificates Only banks can act. Certificates of deposit are intended exclusively for legal entities, and savings certificates are intended for individuals. Certificates must be urgent. The circulation period for certificates of deposit (from the date of issue of the certificate to the day when the owner of the certificate receives the right to claim the deposit) is limited to one year. The circulation period of savings certificates is limited to three years.
- 5. Securities also include check - a written demand from the drawer of the check to the payer to pay the holder of the check the amount specified in it. Checks are always written on forms prepared by banks. It is known that the drawer is the person who issued the check, the check holder is the person in whose name the check is issued, and the payer is the bank or credit institution, in which the drawer has an account.
There are other securities: warehouse receipt(a document certifying the storage agreement concluded between the parties) and bill of lading(a document of title certifying the right of its holder to dispose of the cargo specified in the bill of lading and to receive the cargo after completion of transportation).
Derivatives. These securities include warrant, depositary receipt, futures and options.
Warrant - this is an additional certificate issued along with a security and giving the right to special benefits to the owner of the security after a certain period (for example, to purchase new securities).
Depository receipt - A publicly traded security issued on shares of a foreign company deposited in a depository bank. In world practice, there are two types of depository receipts:
- * American Depositary Receipts (ADRs), which are admitted for circulation only in American stock market;
- * global depositary receipts (GDR), transactions with which can be carried out in other countries.
Futures - a document that provides a firm commitment to buy or sell securities after a specified period at a pre-agreed price. Futures is one of the financial accounting instruments future value securities. An investor receiving a futures contract agrees to buy shares at a future date, with the date of purchase fixed in the contract. The seller of the contract agrees to sell the securities after the period of time specified in the contract at the price at the time the contract is entered into. Thus, a person planning to purchase securities in the future can avoid the risk that their price will increase. However, if their price falls, the buyer loses the opportunity to purchase these securities at low prices.
Option - a bilateral agreement on the transfer of the right to purchase (sell) securities at a pre-fixed price at a certain time. If the price of that security rises, the buyer exercises the written option contract and buys the security at a price below the market price. If the price falls, the buyer may not exercise the option. Thus, by purchasing an option, the investor receives the right to buy from the seller of the option or sell to him an agreed amount of securities at an agreed price or to waive his right. For the opportunity to choose, the investor pays the option seller a premium. Prize - This is the option price paid by the buyer to the seller against the writing of the option contract. According to the expiration dates, the option is divided into two types: American, which can be exercised on any day before the expiration of the contract, and European, which can be exercised only on the day of expiration of the contract.
There are two types of options: put and buy.
Put option gives its owner the right to sell securities or refuse to sell them. Buy option gives its owner the right to buy securities or refuse to purchase them. An investor purchases a buy option if he expects the price of a security to rise, and a put option if he expects it to fall.
They occupy an important place in the market government securities (GS) - debt securities issued by the state. In its own way economic essence All types of government securities are debt securities. In practice, each independent paper receives its own name, which allows it to be distinguished from other types: bonds, treasury bill, certificate and others.
Security is a document certifying, in compliance with the established form and mandatory details, property rights, the exercise or transfer of which is possible only upon its presentation.
Types of securities
IN Civil Code RF lists specific types of documents that relate to securities:
-
bearer bank savings book;
bill of lading;
-
privatization securities;
warehouse receipt as part of a double certificate;
certificate of pledge (warrant) as part of a double certificate;
simple warehouse receipt;
mortgage;
other documents that are classified as securities by laws on securities or in the manner prescribed by them
government bond;
bond;
Properties of securities
Securities have the following properties:
Tradability is the ability of securities to be bought and sold on the market, and in many cases to act as an independent payment instrument.
Availability for civil circulation – the ability of a security to be the object of other civil transactions.
Standardity and seriality.
Documentation; a security is always a document, and as a document it must contain all the mandatory details provided for by law.
Regulated and recognized by the state.
Marketability – securities are inextricably linked with the corresponding market and are its reflection.
Liquidity is the ability of a security to be quickly sold and converted into cash.
Risk is the possibility of loss associated with and inherent in investments in securities.
Mandatory performance.
Profitability – characterizes the degree of realization of the right to receive income by the owner of the security.
Functions of securities
Securities perform a number of essential functions:
Securities characterize the state of the economy. Stable stock prices usually indicate a good economic situation.
Securities play an important role in the redistribution of capital between various sectors of the economy. That is, securities perform a redistribution function.
Securities are used to accumulate temporarily free cash savings of citizens. That is, securities perform a mobilizing function.
Securities are used for regulation money circulation. That is, securities perform a regulatory function.
Banks, enterprises and organizations use securities as a universal credit and settlement instrument. That is, in this case, securities perform a settlement function.
Classification of securities
Classification of securities is their division into types according to certain characteristics that are inherent to them. In turn, species can in some cases be divided into subspecies, and these can be divided even further.
Securities can be classified according to the following criteria:
1. By duration of existence: fixed-term (short-term, medium-term, long-term and revocable) and unlimited.
Securities issued for the entire life of a person and not directly related to any time period are considered perpetual securities. Such perpetual securities usually include shares.
Securities that have a life period established upon their issue or a procedure for establishing this period are considered futures securities. Typically, fixed-term securities are divided into three subtypes:
short-term securities with a circulation period of up to 1 year;
medium-term securities with a circulation period from 1 to 5 years;
long-term securities with a maturity from 5 to 30 years (mortgage-backed securities, by law, can be issued with a maturity of up to 40 years).
2. By form of existence: paper (documentary) or paperless (undocumented).
The classic form of existence of a security is a paper form, in which the security exists in the form of a document. At the same time, with the active development of the securities market, many types of securities, primarily equity securities, are issued in book-entry form.
3. By form of ownership: bearer (bearer securities) and registered, which contain the name of their owner and are registered in the register of owners of this security.
A bearer security does not record the name of its owner, and its circulation is carried out by simple transfer from one person to another. A registered security contains the name of its owner and, in addition, is registered in a special register. Typically, a registered security is transferred by agreement of the parties.
4. According to the form of appeal (order of transfer): transferred by agreement of the parties (by delivery, by assignment) or order (transferred by order of the owner - endorsement).
If a registered security is transferred to another person by making a transfer note (endorsement) on it, or by order of its owner, then such a security is called an order security.
5. By form of issue: emission or non-equity securities.
Issue-grade securities are usually issued in large series, which are subject to mandatory state registration. Equity securities usually include stocks and bonds.
Non-issue securities are issued without any state registration.
6. By registration: registered (state registration or registration of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation) and unregistered.
The issue of securities may or may not be accompanied by their mandatory registration with government authorities. Typically, equity securities are subject to state registration, since their issue affects the interests of a large number of market participants. According to Russian legislation, issued shares, bonds, bank certificates (registered by the Central Bank) and mortgages are subject to mandatory registration. Other types of Russian securities, regardless of the size of their issue, are not subject to state registration.
7. By nationality: Russian or foreign.
8. By type of issuer: government securities (these are usually various types of bonds issued by the state), non-government or corporate (these are securities that are issued by companies, banks, organizations and even individuals).
9. By negotiability: market (freely circulating), non-market, which are issued by the issuer and can only be returned to him (cannot be resold).
The main types of securities are marketable, i.e. securities can be freely sold and bought on the market. However, in a number of cases, the circulation of securities may be limited, and the security cannot be sold to anyone other than the one who issued it, and strictly within a specified period. Such securities are called non-marketable.
10. By purpose of use: investment (the goal is to generate income) or non-investment (serve turnover in commodity markets).
11. By risk level: risk-free or risky (low-risk, medium-risk or high-risk).
Risk-free securities are securities for which there is virtually no risk. In world practice, these are short-term (1-3 months) government debt obligations (treasury bills). All other securities according to the level of risk are usually divided into low-risk (these are usually government securities), medium-risk (these are usually corporate bonds) and high-risk (these are usually shares).
12. Based on the availability of accrued income: non-income or income-generating (interest, dividend, discount).
From the point of view of accruable income, securities, as a rule, are profitable, but they can also be non-income when for their owner they are a simple certificate of goods or money, and not capital. Income from a security may be in the form of a dividend (stock), interest (debt securities) or a discount, i.e. the difference between the par value of the security and the lower purchase price.
13. At par: constant or variable.
According to Russian legislation, each security has its own denomination or face value. However, in world practice it is allowed to issue, for example, shares without a monetary par value or with a zero par value. In this case, it is indicated what share in the authorized capital is one share, and therefore its par value, calculated by dividing the authorized capital by the number of shares, changes each time the size of this capital changes, and does not remain unchanged as in the case when the par value of the security is given upon its release. If a security is issued with a monetary denomination, then such security is considered a security with a constant denomination. If a security is issued without a monetary par value (zero par value), then such security is considered a variable par value security.
14. By the form of raising capital: equity (reflecting the share in the authorized capital of the company) and debt, which are a form of borrowing capital (cash).
Book of securities accounting
All securities held by the organization must be described in the securities ledger.
The securities accounting book must have the following mandatory details: name of the issuer; nominal price of the security; purchase price; number, series, etc.; total quantity; date of purchase; date of sale. The securities accounting book must be bound, sealed with the organization's seal and signed by the manager and chief accountant, and the pages must be numbered. Corrections to the securities accounting book can be made only with the permission of the manager and chief accountant, indicating the date of the corrections.
In the case of maintaining a securities ledger using computer technology, the resulting information can be generated in the form of an output document on machine-readable media. Printing of information from machine-readable media is carried out as necessary or at the request of the authorities exercising control in accordance with the law. Russian Federation, courts and prosecutor's offices, but at least once a year.
According to Federal law“On Accounting”, the head of the organization is responsible for organizing the storage of the securities ledger.
Still have questions about accounting and taxes? Ask them on the accounting forum.
Securities: details for an accountant
- Impossibility of paying personal income tax on income received from the sale of securities
Individuals arising from the sale of securities. I quote: “For the purposes of this... Russian Federation of shares or other securities...”. Pay attention to the term... individuals arising from the sale of securities. I quote: “For the purposes of this... Russian Federation of shares or other securities...”. Pay attention to the term... income of an individual from the sale of securities, and individual sales, ... Russian Federation, income from the sale of securities by individuals was not subject to taxation ...
- Review of letters from the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation for July 2019
The creditor has the right to claim securities arising from an agreement for the sale of securities exempt from taxation... directly related to transactions with securities and financial instruments of futures transactions...
- Personal income tax in 2018: clarifications from the Russian Ministry of Finance
From transactions with securities carried out by a professional participant in the securities market within the framework of... transactions with securities by a Russian broker and for what securities (Russian or... foreign financial instruments as securities", if the qualification of foreign... income received by the taxpayer upon the sale of securities are included in the taxpayer’s income, ..., the taxpayer’s expenses for the acquisition of securities include the amount of accumulated interest (...
- Submission by civil servants of information on income for 2018
Real estate, vehicles and securities alienated during the reporting period... is indicated. The securities themselves are reflected in section. 5 “Information about securities” (in case... and (or) an agreement trust management securities, including an agreement to maintain an individual... - Federal Law “On the Securities Market”, a share is an issue-grade security that secures the rights of its owner... certificates. Subsection 5.2 “Other securities”. Securities include shares, bills, mortgages...
- Income tax in 2017. Explanations from the Russian Ministry of Finance
28201 Scope of rights granted to holders of securities additional release, cannot... differ from the scope of rights provided by the securities of the main issue. In particular, ... interest (coupon) income on securities tax agent must calculate the amount... of income on securities, calculated based on the period of ownership of this security foreign organization... income on securities, calculated based on the period of ownership of this security by a foreign organization...
- Audit of annual financial statements of organizations for 2018
Audit financial statements organizations whose securities are admitted to organized... contracts bank deposit, debt securities, financial liabilities valued by... , bank deposit agreements, debt securities, financial liabilities valued by... bank deposit agreements, debt securities, financial liability upon initial recognition... as property; management of funds, securities or other property of the client; ...
- Review of letters from the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation for December 2018
The composition of the total expenses for the sale of securities exempt from taxation... from transactions with securities carried out by a professional participant in the securities market within the framework of brokerage..., sale, storage and redemption of securities, with transactions with derivatives... a Russian broker carries out operations with securities and for what securities (Russian or... cooperatives and mutual funds, securities and derivative financial instruments...
- General and special income tax rates
...: government securities of member states of the Union State; government securities of constituent entities of the Russian Federation and municipal securities... Russian organizations, investment units that are securities of the high-tech (innovative) sector of the economy. Rate... of Russian organizations, investment shares that are securities of the high-tech (innovative) sector of the economy (with... % 0% Income on securities Clause 4.2 Income on securities (except for dividends...
- Bypassing the treasury: how an investor can save on taxes
Tax deductions for the sale of securities purchased after January 1... are paid by the company itself - the issuer of the securities. Tax liability on income from... in the tax office. For security holders Russian legislation provides for a number of tax... investment tax deductions for owners of securities traded on their organized... with IIS, and the acquisition of securities of foreign issuers is allowed only on... tax deduction when selling securities purchased after January 1...
- Capital amnesty: last chance
... – voluntary declaration foreign real estate, securities, bank accounts, foreign companies, ... - voluntary declaration of foreign real estate, securities, bank accounts, foreign companies, ... benefits received from the acquisition of securities from such a foreign organization ... - voluntary declaration of foreign real estate , securities, bank accounts, foreign companies... accounts, foreign property (real estate, securities, assets), foreign companies(KICK...
- “Trojan horses” in auditing, consulting and assessing the value of economically significant enterprises and companies in Russia
In the direction of “Business and Securities Valuation”. The unsatisfactory performance of the domestic rating... is noted in determining the cost property complexes and securities of the country's enterprises in 2017... IN THE DIRECTION "ASSESSMENT OF BUSINESS AND SECURITIES" No. Company / group of companies Type... "Evaluation of business enterprises and their securities." First of all, it is necessary to create an All-Russian..., in the direction of “Business and Securities Valuation”. The unsatisfactory performance of the domestic rating...
- Review of letters from the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation for April 2018
Foreign financial instruments as securities" if the qualification of a foreign... foreign financial instrument as a security may be carried out by the Bank... of a foreign financial instrument as a security was not confirmed in... income received by the taxpayer upon the sale of securities are included in the income of the taxpayer, ... accordingly, the taxpayer’s expenses for the acquisition of securities include amounts of accumulated interest (...
- Cases of mandatory property valuation
Payment for shares and other issue-grade securities of the company upon their placement "... of the company may be money, securities, other things or property... in relation to foreign currency and securities in foreign currency) on... in relation to foreign currency and securities in foreign currency), for which... the executive body for the securities market of property owned by the joint-stock investment... executive body for the securities market. Equity appraiser investment fund...
- Review of letters from the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation for May 2017
28201 The scope of rights granted to holders of securities of an additional issue cannot differ... from the scope of rights provided by securities of the main issue. In particular, the tax agent must... interest (coupon) income on securities must calculate the amount... income on securities calculated based on the period of ownership of this security by a foreign organization... collected by the Bank - a professional participant in the securities market from client when transferring income...
- Legal status of cryptocurrency
Valuables, Russian currency and domestic securities as a means of payment; acquisition... by authorized banks professional participants in the securities market) from residents and non-residents of information... value ( foreign currency and an external security), therefore, making a payment using... including cash and certificated securities, other property, including... non-cash funds, uncertificated securities, property rights; results of work and...
The unified procedure for the issuance and circulation of securities, as well as regulation of the activities of professional participants in the securities market in the Republic of Belarus, is determined by the Law of the Republic of Belarus of March 12, 1992 “On Securities and Stock Exchanges” (as amended and supplemented).
Securities - monetary documents, certifying the property rights or loan relationship of the owner of the security in relation to the issuer expressed in them and realized through presentation or transfer. Issuer of securities - a legal entity that issues securities on its own behalf and undertakes to fulfill the obligations arising from the terms of the issue of securities. Investor - an individual or legal entity that owns securities. Securities may be issued in the form of printed forms on paper or in the form of entries in accounts.
Features of the security:
It contains a certain property right;
Possession of this right and its exercise is associated with ownership of the security;
This is a document of the established form and contains mandatory details;
Securities are authentic in form and do not require additional confirmation of the rights of their holders.
TO securities include : shares, bonds, bills, checks, bills of lading, warehouse receipts (warrants), letters of credit; lottery tickets(if they win).
Not applicable for securities - promissory note, cashier's check, because they are evidence of a legal relationship, but do not embody property rights.
Securities can be: bearer , order , personalized.
Bearer are written out without indicating the person who should perform the execution, and therefore carry out the expressed
any person presenting them may have rights in them. They have increased defensive capability, since they are transferred by simple delivery to the new owner.
Warrants are issued to a specific person, but with a simultaneous indication that execution on them can be made not only to the designated person, but also to his “order” (order) to any other person; it is enough to make an endorsement on the security itself, which can be done by any subsequent holder. Order papers have advantages over bearer papers:
Not only the debtor is responsible for them, but also the persons under the endorsement, unless they have made a reservation (without reference to me) that eliminates liability. The bearer of the order paper may apply
to any “signer” in case of non-payment by the debtor (bill of exchange).
Registered security is issued in the name of a specific person who alone can exercise the right expressed in it. Its transfer is practically impossible (they are non-negotiable or complicated negotiable).
Brief description individual species securities:
A. Bond - a security certifying the right of its owner to receive from the person who issued the bond its nominal value within a certain period, as well as interest on the value or other property right. Bonds are issued in series consisting of homogeneous securities with equal par value and the same terms of issue and redemption.
Types of bonds: registered, bearer, interest-bearing, interest-free (target), freely circulating, with a limited circle of circulation.
B. Check - a document containing an unconditional order from the owner of a current account to the bank to pay a specified amount to a specific person or bearer. Check drawer - legal entity or individual, including individual entrepreneur making payment for goods or services by check. Types of checks : bearer - to bearer, transfer by simple delivery; personalized - to a specific person; order - in favor of a certain person or on his order.
IN. By bill of exchange is a document drawn up in the form established by law and containing an unconditional obligation or instruction of the drawer to pay the owner of the bill (bill holder) a certain amount within a specified period. A promissory note can be expressed either in the form promissory note (solo bills), or in the form bill of exchange (drafts).
Promissory note written out and signed by the debtor
and represents his obligation to pay the specified amount on time to a certain person or, on his order, to another person, the name of the payer and recipient is indicated.
Bill of exchange is issued and signed by creditors and represents an order from the creditor (drawer-drawer) to the debtor (drawee) to pay a certain amount to a third party within a specified period, only the payer is indicated.
When making an endorsement, the person (endorser) to whom the bill of exchange is transferred acquires all rights of claim under the bill. Endorsement must be written on the reverse side of the bill or a sheet attached to it and signed by the endorser and must not contain any conditions for its validity. The debtor's refusal to pay or accept a bill must be certified by an official act certifying the fact of refusal to pay or accept, protest in non-acceptance or non-payment. The protest must be made by notary authorities. Timely execution of a protest allows the holder of the bill to bring a claim against any of the persons responsible for payment - endorsers, drawer, guarantors.
G. Promotion - a security indicating the contribution of a certain share to the capital of a joint-stock company. Gives the right to receive part of the profit in the form of a dividend.
Types of shares:
· founding shares (distributed among the founders);
· preferred - holders receive dividends as a matter of priority, regardless of the profit of the enterprise, but are deprived of the right to vote in the management of the joint-stock company;
· bearer - to a bearer whose name is not indicated;
· ordinary, simple - nominal;
· without indicating a nominal price.
D. Treasuries states - government securities that give their owners the right to receive a fixed income during the entire period of their ownership. They are always bearer securities. They are issued not by banks, but by the Ministry of Finance of the republic. The amounts received from them are credited to the state budget, at the expense of which payments are made on them. These are means of lending by the population of the state.
E. Savings and certificate of deposit jar written certificates from the bank certifying the depositor's right to receive, upon expiration of the established period, the deposited amount (free funds of citizens and organizations deposited in the bank) and interest on it.
AND. Bill of lading - a document defining the relationship between the carrier and the cargo owner in the process of transporting cargo in international shipping, giving its holder the right to dispose of the cargo specified in it, including the right to receive it from the carrier.
Species: registered, bearer, order.
Z. Warehouse receipt (warrant ) is issued by a commodity warehouse (custodian) to confirm the fact of concluding a storage agreement and accepting goods for storage, and the holder of the certificate receives the right to dispose of the goods at the same time when the goods are in storage.
State regulation of the securities market papers is carried out in order to fulfill the requirements of laws and other regulations that define the rights and obligations of each professional participant in the securities market in a number of areas, starting from registration of the issue of securities and ending with the rights of government bodies to regulate the securities market.
Tasks of the bodies government regulation :
· establishing mandatory requirements for the activities of issuers, professional participants in the securities market and its standards;
· registration of issues of issue-grade securities and prospectuses and monitoring of compliance by issuers with the conditions and obligations stipulated therein;
· licensing of activities of professional participants in the securities market;
· creation of a system for protecting the rights of owners and monitoring compliance with their rights by issuers and professional participants in the securities market;
· prohibition and suppression of the activities of persons carrying out entrepreneurial activity on the securities market without appropriate licenses.
Securities market participants:issuers; investment institutions; organizations specializing in serving the market; self-regulatory organizations; government bodies regulation and control; market infrastructure; investors.
Issuers - This legal entities who feel the need to attract financial resources based on the issue of securities. Investment institutions - financial intermediaries who, at their own peril and risk, perform strictly defined functions in the securities market, both through own funds, and through a loan. These are financial brokers, dealers, investment consultants, investment companies, investment funds and their managers.
Organizations specializing in serving the market:
Stock exchanges,
Stock departments of commodity exchanges,
Currency exchanges,
OTC markets,
Specialized registrars,
Settlement and depository centers,
Information centers.
Species professional activity on securities:
· intermediary;
· commercial;
· activities of the investment fund;
· activities of the depository;
· fiduciary (trust) activity;
· activities of a specialized registrar.
Brokerage activities It is recognized that civil transactions with securities are carried out as an attorney or commission agent acting on the basis of an agreement or commission, as well as a power of attorney.
Dealer activities It is recognized that transactions for the purchase and sale of securities are carried out on one’s own behalf and at one’s own expense by publicly announcing the purchase and/or sale prices of these securities at prices announced by the person carrying out such activities.
Clearing- a variety of operations the purpose of which is settlement for delivered securities. In this case, no money transfer or delivery of funds is made. Clearing activities - this is an activity to determine mutual obligations, including collection, reconciliation, and adjustment of information; drawing up a payment schedule; acceptance for execution when determining mutual obligations accounting documents; the formation of special funds that serve to reduce the risks of non-fulfillment of obligations of the parties when making transactions with securities; control over the movement of securities, etc.
Depository activities activities related to the provision of services for storing securities certificates and/or accounting and transfer of rights to securities are recognized. The depositary bears civil liability for the safety of the certificates deposited with it.
Trust(trust ) activity - this is the activity of managing securities owned by a specific person by right of ownership, carried out by another person by transferring these securities to him for a certain period of time for possession and trust management.
Issue of securities into circulation or emission
is the sale of securities to their first owners. The issue of securities can be carried out when a joint stock company is established, when its size increases authorized capital, as well as when attracting borrowed capital by various issuers (including the state
and local governments) by issuing debt securities.
Issue procedure includes the following steps:
· the issuer's decision to issue securities;
· registration of securities;
· placement of securities;
· registration of a report on the results of the issue.
· the decision to issue securities is made by the authorized body of the issuer.
Prohibition or suspension of the issue of securities carried out by the central regulatory authority in the event of:
· violations of current legislation;
· absence or discrepancy of the information presented in the prospectus with the actual state of affairs:
On the financial and economic condition of the issuer (losses, profits) over the last two completed years;
On the presence of overdue debts to creditors and payments to the budget;
On the presence of an incompletely paid authorized fund at the time of making the decision to issue bonds.
A ban based on the inexpediency of issuing securities is not permitted. In case of suspension of the issue of securities, the issuer is obliged to eliminate the violations, and then, with the written permission of the central authority, continue the issue. In case of disagreement with the decision of the body that suspended the issue of securities, the issuer may challenge this decision in court.










Carrying out an inventory
Ulyukaev, Navka and Patrushev
Income tax refund for treatment: registration procedure and calculation of the deduction amount
Import substitution - what is it?
OSAGO minimum insurance period