Building survey- this is a specific list of operations, the purpose of which is to check the condition and defects of both the buildings themselves and any of its structural elements.
There are several main objectives of the survey:
- Inspection and research before putting buildings into operation;
The main task is to check the compliance of the constructed building project documentation and also identify violations.
- Inspection and research of buildings that have already been built.
Determining the deterioration of the building, the possible load-bearing structure of the building elements, taking parameters for the reconstruction of the building. Scheduled and unscheduled inspections.
- Various laboratory tests of structural elements;
There are basic requirements for buildings and structures that must not be violated:
- All buildings and structures must be strong and stable.
- Lagging behind the building are cracks and damage.
All other deviations from the normal state of objects should be examined by trained engineers with experience working on the relevant objects and having specialized equipment available.
Any examination consists of several elements:
- Primary. Study of design documentation, familiarization with the repair work carried out.
In this case, it is possible to determine the weak areas of the design schemes, as well as the places of maximum load and the theoretical degree of wear.
- Visual inspection. An engineer examines the compliance of the object working documentation, searches for defects, draws up a plan for a more detailed examination. All surveys are carried out using non-destructive methods.
Important. Non-destructive methods are any types of examinations that do not require direct disabling of operating objects, without physical sampling of materials.
The visual examination includes:
- Carrying out measurements of the property and subsequent production.
- Drawing up a list of defects with photographic recording.
- Assessing the reliability of building elements.
Upon completion of the visual inspection, the customer is provided with
- List of defects, with a description of their nature, location on the diagrams;
- Photo recording with the class and characteristics of defects;
- Description of possible deformations of the building or its individual elements (deflections, tilts, bends, distortions, faults, etc.);
- Identification of emergency areas;
- Updating and sectional diagrams of the building;
- Determination of load-bearing walls and structures with location on the drawings;
- Preliminary analysis of the condition of load-bearing structures and utility networks;
- Recommendations, estimates for eliminating identified deviations;
- Full analysis with testing of structural elements and development possible ways solving the assigned problems.
Definition design features parts of the building, assessment of the technical condition of the load-bearing and enclosing structures of the building to calculate the loads on the floors. Structural elements are subject to technical inspection: foundations, floors, walls.
Scope of services in case of full technical inspection:
- List of works when inspecting base soils and foundations with
- digging 4 pits for the building:
- Analysis of engineering and geological conditions of the site ( land plot under the building);
- Carrying out research pits to clarify parameters
- foundation;
- Selection of soil samples from under the foundation soles to clarify properties
- soils;
- Performing laboratory tests of foundation soils.
- Foundation material testing;
- Dynamic sensing to a certain depth (depending on the size and height of the building);
- Carrying out verification calculations to determine the design resistance and maximum ground pressure.
- Inspection of the technical condition of engineering networks.
- Installation of deformation marks on the main structures of the building. (average 20 pieces)
- Installation of geodetic marks
- Leveling class II (building settlements) (depending on the number of corners of the building)
List of works during visual and instrumental examination of the above-ground part of the building:
- Inspection of the technical condition of the building.
- Inspection building structures with sketches of defects and damage, photographic recording of defects and preparation of a defect sheet;
- Determination of the strength of walls using non-destructive methods;
- Carrying out openings of floors to clarify its composition and
- determination of bearing capacity.
- Sampling from structures for mycological studies - the number of samples for the laboratory is specified based on the results of autopsies.
- Measurement work required for the survey
- Analysis of archival materials.
- Necessary calculations load-bearing structures(floors, walls).
- Determination of the building category based on the technical condition of structures according to TSN 50-302-204, GOST R53778-2010.
Sample estimate for building inspection
The estimate is compiled in prices for the third quarter of 2015. Prices are given per 100 m3 of building.
The estimate is based on the Directory base prices for measurement work and inspection of buildings and structures, State Enterprise "Tsentrinvestproekt", M., 1998.
The total volume of the building is 74,940 sq. m. m.
Sample terms of reference (for drawing up tender documentation):
In case of visual inspection:
Option 1
Terms of reference
- Place, conditions and timing of work
1.1. Place of work: __________________________
1.2. Time frame for completing the work: __________________________
1.3. The contractor is obliged to perform a visual inspection of the main load-bearing structures of the building with photographic recording, drawing up a report with conclusions and recommendations, developing statements and diagrams of defects non-residential building at the address: st. Millionnaya 30 lit.A.
1.4. Main technical and economic indicators of the building being examined:
Year of construction – _____, capital year. repair – _____
Total area – ____
Purpose – __________________
2. Requirements for the description of work performed
2.1. Name of work performed: Conducting a visual inspection of the main load-bearing structures of a non-residential building in accordance with the requirements of GOST 31937-2011.
2.2. Requirements for the work performed:
2.2.1. An organization that meets the requirements established by law is allowed to carry out work. Russian Federation requirements for design organizations, having a valid Certificate of Admission to perform this type of work.
2.2.2. The Contractor transfers to the Customer the design documentation developed by him in 3 copies on on paper and 1 copy on electronic media.
2.3. List of structures inspected and scope of work:
2.3.1. Inspection of concrete and reinforced concrete structures(according to clause 5.3.1. and appendix E GOST, without opening)
2.3.2. Inspection of stone structures ( without opening or probing)
2.3.3. Inspection of steel structures (according to clause 5.3.3 and appendix Zh GOST, without opening)
2.3.4. Inspection of wooden structures (clause 5.3.4., without opening or drilling)
2.3.5. Inspection of building elements of balconies, bay windows, loggias - clause 5.3.5., without opening
2.3.6. Inspection of stairs - clause 5.3.5. without opening
2.4. The result of the visual inspection is the development of a report on the technical condition of the main load-bearing structures of the building with:
— indicating the structural diagram of the building and describing the load-bearing structures of the building by floor;
— compilation of lists of defects and damages according to external signs with their measurements and recording on diagrams;
— description of emergency areas (if any);
— developing conclusions about the condition of the building;
After conducting an inspection of the technical condition of the building, the information in the developed report should be sufficient to make an informed decision about the possibility of its further trouble-free operation.
The report is transferred to the Customer according to the Acceptance Certificate.
Sample technical specification Option 2
Terms of reference
Price guide for inspection of buildings and structures
Directory of basic prices for measurement work and inspection of buildings and structures, State Enterprise "Tsentrinvestproekt", M., 1998.
Final cost work is determined using the coefficient approved in a letter from the Ministry of Construction of Russia. The latest edition of the letter and the required coefficient can be found on the Internet.
Result of technical inspection of buildings and structures
In a request for a commercial proposal, we only need a few characteristics: Address of the property, area of the property, number of floors, as well as the required type of survey.
Inspection of buildings and structures is a complex engineering work by assessing their technical condition (load-bearing structures, hulls, foundation soils, bearing capacity). A comprehensive inspection of buildings and structures, unlike the previous type (according to GOST 31937-2011, there is a simple and comprehensive inspection), also includes determining the technical condition of internal engineering systems/equipment and determining the thermal and acoustic properties of structures.
Inspection of buildings and structures is carried out using modern technologies:
- laboratory for testing building structures and foundation soils;
- non-destructive and destructive testing;
- photographic recording of defects;
- external inspection.
When is an examination necessary?
- Before reconstruction, major repairs, modernization;
- before putting into operation;
- to control the quality of work performed;
- in case of a dispute between the customer and the contractor;
- for the purpose of assessing damage caused by a natural disaster, fire, improper operation, design errors;
- when defects and damage occur in structures;
- when buying and selling;
- for the purpose of restoring design and executive documentation;
- to clarify the cost of work performed and construction materials;
- when restoring lost design and as-built documentation;
- to identify deviations from design and estimate documentation.
Frequency of examination
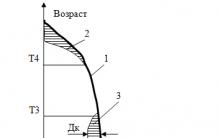
The frequency is established by GOST R 53778-2010 and GOST 31937-2011. The first inspection of a new serviceable facility must be carried out no later than two years after commissioning, subsequent inspections at least once every 10 years under favorable operating conditions and once every 5 years under unfavorable ones. If cracks, kinks or deformation of the structure are detected, immediate research work is necessary to avoid an accident.
The validity period of a building inspection depends on what category of condition it was assigned to and how high the need for re-inspection in the near future is. According to document RD 22-01.97 maximum term The validity of research results is 5 years.
Stages
Technical inspection of buildings and structures is carried out in 4 stages:
- preparatory work;
- visual inspection - assessment by external signs;
- detailed examination - assessment based on instrumental analysis;
- desk processing of data - preparation of documentation, development of recommendations.
Preparatory work
All preparatory work can be divided into 4 stages:
- getting to know the object;
- working with the archive;
- analysis of design technical documentation;
- development of a program of future actions.
Before starting work, you should familiarize yourself with the following types of documents:
- design and executive documentation for the design and construction of a building (structure);
- operating documentation;
- documentation of repairs and reconstructions that took place;
- reports from previous inspections.
Project documentation allows you to establish:
- developer and year of development;
- design diagram and geometric dimensions of the object;
- assembly diagrams of prefabricated elements;
- calculation schemes;
- design loads and characteristics of all components (stone, concrete, reinforcement, etc.).
The following information can be found in the technical documentation:
- terms of Use;
- engineering and geological operating conditions;
- data on deviations from the project;
- indicators of design loads and their impacts according to PD;
- equipment locations.
In addition to these documents, the following are studied:
- work acceptance certificates;
- acts for hidden work;
- passports for prefabricated elements and materials;
- building passport;
- work production log;
- documents on repairs and reconstructions carried out.
Based on the results of familiarization with the object and work with the archive and documents, a technical inspection program for the object is drawn up, which includes all stages of external and internal visual and instrumental inspection of the building.
Visual inspection
Visual inspection of buildings and structures is the process of inspecting the technical condition of buildings without the use of tools and carrying out verification calculations. The main purpose of the study is to identify deviations from the design documentation and the need to conduct a detailed study.
Carrying out a technical inspection of buildings includes:
- ensuring access to structures (scaffolding, devices, technological platforms, overhead crane), turning off the power supply and providing heating if necessary;
- visual inspection and recording of defects;
- measurements of the dimensions of buildings and structures;
- determining the condition of soils and structures by external signs;
- drawing up a map of damages and defects by applying them to façade diagrams and plans;
- drawing up a defective list in the form of a table indicating methods for eliminating identified damage;
- photographic recording of damage;
- drawing up a conclusion.
Based on the initial examination, if necessary, a detailed examination program is drawn up.
Detailed examination
A detailed examination is an assessment of the technical condition of a building based on instrumental and laboratory tests and calculations. The inspection of buildings ends with the writing of recommendations for correcting damage and further safe operation.
Carrying out a building inspection includes the following steps:
- measuring work with the preparation of floor plans, facades, sections;
- opening of reinforced concrete structures - determining the quantity, class, diameter of reinforcement, depth of carbonation of concrete, etc.;
- opening the roof and floor, determining the condition and degree of load of the coating on the floors;
- opening and evaluation of individual components of building structures;
- digging holes for the foundation, taking soil samples;
- instrumental inspection of buildings - the use of shock-pulse, ultrasonic methods, and the rib chipping method;
- determination of the strength characteristics of metal structures (sampling for laboratories, sampling of shavings for chemical analysis);
- identifying heat leaks using thermal imaging inspection;
- drawing up an actual design scheme, carrying out verification calculations;
- drawing up a map of defects and damages;
- drawing up a defect report;
- drawing up a technical report.
Desk verification calculations
Desk verification calculations include:
- assessment of technical condition;
- data analysis and processing;
- development of an engineering solution;
- preparation and issuance of a conclusion.
Desk calculations include verification statistical calculations of building structures using software systems and thermal engineering calculations of enclosing structures.
Technical report
The result of the study is an inspection report of the building or technical report. The first option is used when a small volume or part of a structure is examined, the second when in-depth research.
The technical report for the inspection of the building contains text and graphic parts.
The text part includes:
- object description;
- results on foundations and soils;
- data on walls and partitions;
- information on columns and pillars;
- coating and roofing results;
- conclusions;
- recommendations.
Documentation contains detailed descriptions identified defects and damage, shortcomings, descriptions of materials, calculation results, strength characteristics, etc.
Graphic summary of the survey:
- results of measurement work (drawings, facades, components);
- maps of defects and damages;
- list of defects and damages;
- verification calculations;
- instrumental tests;
- ultrasonic testing;
- results of geophysical studies of foundations and buried structures;
- laboratory test results.
The conclusion is the main document on the basis of which conclusions are drawn regarding further interaction with the building/structure. Subsequently, it is submitted for expert assessment and accepted for work.
A visual inspection of buildings and structures allows us to give a preliminary assessment of their technical condition. Simple actions without the use of complex equipment often reveal structural defects that can lead to the destruction of an object.
Importance of Visual Inspection
An unprepared customer often perceives inspection of an object with the naked eye as something useless. He has more confidence in a specialist with a device in his hands. Meanwhile, visual inspection has a number of important advantages:
- during its implementation, the object is examined completely, and not selectively, as is done during instrumental research;
- only with its help can one detect areas subject to instrumental research and the scope of this type of work;
- the emergency condition of structures is determined by the presence of cracks, defrosting of masonry and other defects without the use of expensive equipment - the eyes of an experienced specialist are enough for this;
- The purpose of the technical inspection is to determine the category of technical condition.
Often the purpose of the work is to assess the category of technical condition of structures. The corresponding conclusions can be drawn based on the results of a visual examination. Neither complex calculations nor instrumental control will be needed in this case.
Procedure
The quality of the visual examination depends on strict adherence to the sequence of operations. First, a total inspection of the object is carried out, and a list is compiled
- A full site inspection is carried out. All defects that come into view are entered into a list.
- The first results are analyzed: the degree of significance of the defects is assessed, the causes of formation are determined, and the structures on which they were found are noted.
- The technology for fixing defects is selected - element-by-element, floor-by-floor, end-to-end or other numbering system, using symbols, etc.
- The basis for damage and defect maps is being developed.
- Defective maps are drawn up
- At the same time, the damaged areas are photographed.
- Using tools, defect parameters are measured (corrosion depth, crack width, etc.).
- Conduct geodetic measurements of changes in shape (deformation) of building structures.
- Defective statements and cards are drawn up.
A map of defects is drawn up separately for each type of structure: floors, walls, roofing, which allows a more detailed assessment of the volume and the need for a detailed examination of each structure.
Survey results
After processing the received data, the customer is issued a conclusion, which reflects the technical condition of the object as a whole and its individual building elements. In addition, the document contains recommendations on:
- the possibility of further operation and the conditions under which it remains safe;
- the need for a detailed survey and its methods, indicating the places subject to it;
- priority measures to ensure the continued use of the facility
If no additional research is required, the conclusion of the visual inspection is considered final.
Inspection of building structures, including buildings, is carried out in order to determine the actual values characterizing the at this stage, operational condition of buildings. The need for such an examination is associated with determining the possibility of continuing operation without making any changes to the design or with recommendations for restoring or strengthening the existing structure.
In modern construction, a mandatory justification for conducting a visual inspection is required.
An inspection of building structures, including buildings, is carried out in order to determine the actual values characterizing, at this stage, the operational condition of buildings. The need for such an examination is associated with determining the possibility of continuing operation without making any changes to the design or with recommendations for restoring or strengthening the existing structure. The main directions that guide the preliminary examination are:
Identification of possible defects and damages that occur after exposure of building structures to man-made (fires, soil subsidence) or natural (flood) influences.
Increased loads associated with redevelopment or increasing the number of floors.
Proposed or completed reconstruction.
Resumption construction work on site, after long-term conservation.
Survey process
Preliminary (visual) inspection of buildings involves a set of works related to the inspection appearance. In this case, conventional measuring instruments are used (tape tapes, probes) and instruments that allow for a detailed inspection of the appearance of buildings (binoculars, camera, level). The examination is carried out by qualified specialists. In this case, the following are subject to visual inspection:
Foundations.
Floors.
Pillars, columns, walls.
Beams, trusses.
Connecting elements and stiffening structures.
All joints, connections, nodes available for inspection.
All detected defective areas are subject to careful measurement, description, photography, followed by drawing up diagrams of their location. A statement is drawn up indicating the technical parameters of the damage. A preliminary (visual) inspection of buildings is also carried out to identify deformation of the entire building structure (tilting, deflections, faults) and its individual structures. A reconnaissance survey of the facility is being carried out. Guided by the results of the survey, a preliminary conclusion is drawn up on the technical condition of the object being examined. Based on this conclusion, a decision is made to eliminate existing shortcomings, without conducting additional research. Or, a decision is made about the need for a more thorough instrumental examination.
Ask our geologists questions
The cost of the work carried out directly depends on the technical condition of the object itself, its location, and the purpose of the building inspection. You can order such work from companies that have a license to conduct such research. Price for this type work is quite high, but the estimate is drawn up taking into account the full survey cycle, which also includes geodetic survey of the object. Upon completion of the work, the customer is issued a technical inspection certificate of the facility.
Contacting qualified specialists will protect your project for many years and will allow you to implement any project. We recommend turning your attention to the company leader in the field of geodetic research - LLC "Geologist" It is also very convenient that specialists work in many regions and cities of our country: Moscow, St. Petersburg, Moscow region, Yaroslavl region, Tula region, Tver region, Kaluga region, Ryazan region, Bryansk region, Vladimir region, Nizhny Novgorod region, Voronezh region, Kursk region, Tambov region, Belgorod region, Penza region, Krasnodar region, Leningrad region, Pskov region.
During the operation of a building or structure, it is constantly exposed to external factors (rain, snow, temperature changes, etc.), its materials are subject to corrosion, mechanical damage and destruction. Therefore, it is necessary to conduct periodic inspections to identify defects and the degree of wear. Based on its results, a decision is made on further operation of the building or major repairs. Today the simplest and in an accessible way diagnostics is a visual inspection of buildings.
When is a visual examination performed?
It is necessary to conduct a visual inspection of buildings when carrying out construction, repair, and restoration work. A timely inspection will make it possible to identify destructive processes at the initial stages, prevent the occurrence of dangerous situations, and also avoid expensive repairs associated with excessive wear and tear or partial destruction of the building.
A visual inspection allows you to identify visible deformations or defects in building structures. During its implementation, measurements are taken, photographs of dangerous areas are taken, the degree of damage to the building is studied, and recommendations are developed for their elimination. The procedure is carried out in a number of cases.
- When a decision is made about the advisability of purchasing a property. Such research allows potential buyer receive objective information from independent experts about the condition of the building, the presence of defects. Thanks to this, you can avoid unwanted acquisitions and determine whether the buyer’s price corresponds to the real value of the property.
- When you need to make quick decisions to eliminate bottlenecks that can cause accidents.
- If you need to determine the scope of work to repair a building.
- If you need to identify areas that should be repaired first.
Visual examination is the first and easiest way to diagnose. If serious defects are identified at this stage, a decision may be made on a more in-depth inspection and instrumental examination.
Prices
| 1. | Checking the alignment of construction axes and marks of a country house. | 24,000 rub. | 30,000 rub. | 36,000 rub. | Builds over 6. axles, 3 tr are added to each axle. |
| 2. | Foundation examination. | 24,000 rub. | 30,000 rub. | 36,000 rub. | |
| 3. | Identification of construction defects. | 24,000 rub. | 30,000 rub. | 36,000 rub. | |
| 4. | Earthworks, installation of formwork, reinforcement, concrete work (if completed concrete works). If necessary, calculate the ventilation ducts of the basement floor. | 24,000 rub. | 30,000 rub. | 36,000 rub. | |
| 5. | Analysis of design and construction solutions. Recommendations. | 24,000 rub. | 30,000 rub. | 36,000 rub. |
What work is being carried out
The external examination includes the following activities:
- study of design and technical documentation;
- study of engineering and geological surveys;
- measuring work;
- study of the geometric parameters of the building;
- determination of the design diagram;
- identification of defects and damage;
- drawing up a defect report;
- assessment of the general condition of the structure based on visual signs.
Based on the results of the work carried out, a conclusion is drawn up, which contains information about the condition of the building, its main elements and provides conclusions and recommendations for further operation and repairs. In conclusion, an expert conclusion may be given on the need to conduct a detailed comprehensive study.
Order a visual examination
The LLC ExpertStroy-Engineering company offers services for visual inspection of building structures at competitive prices. The cost depends on the area of the object, its location, the technical condition of the structure, the nature of the study and other factors. Carrying out diagnostics will allow you to avoid emergency situations and damage associated with the destruction of the building and harm to third parties. If defects are identified in a timely manner, their prompt elimination will avoid huge costs for major renovation and carefully plan the timing and budget of the current one. The inspection time frame for each case is calculated individually.
We employ experienced engineers and experts with highly qualified who are able to cope with a task of any complexity. They will quickly and professionally inspect the building, identify defects and potentially dangerous areas and give qualified recommendations on how to eliminate them with minimal time and money.










Carrying out an inventory
Ulyukaev, Navka and Patrushev
Income tax refund for treatment: registration procedure and calculation of the deduction amount
Import substitution - what is it?
OSAGO minimum insurance period