Natalia Zaitseva Head of the corporate borrower analysis department of TransCreditBank OJSC, graduate student of the State Financial Academy
Magazine “BDM. Banks and the business world", No. 12 for 2007
However, if we consider the distribution of investments by industry, a certain imbalance is noticeable, which can be explained, first of all, by differences in the level of profitability and risk of enterprises. The most attractive sectors for investors continue to be the raw materials sector, industrial production and transport.
There is no need to dwell in detail on how positively attracting investment resources affects the development of an enterprise. This is obvious. In the most general form, among the positive consequences, experts include the possibility of expanding production, updating basic production assets, development and implementation of new technologies, improving the quality and competitiveness of products, and so on. On the other hand, the benefit the investor receives in the form of income and compensation for the risk taken is also well known.
However, the investor and the “potential investment object” do not always find each other in complex system investment relationships. Why? The investment process is complicated by several factors that an investor faces during the decision-making process. One of them is the choice of an investment object, or, in other words, an investment-attractive enterprise. Everyone knows that when making such a decision, an investor is based on the ratio of risk and return. However, given the presence of a large amount of information and many enterprises operating in the market, accept the objective and most effective solution it can be extremely difficult.
When investing in securities of “first” and, in some cases, “second echelon” issuers, the question of assessing investment attractiveness is rhetorical and does not require any explanation. Such investments are considered low-risk and bring the investor, although stable, but far from the highest income. For example, the total income of owners of “second-tier” bonds, according to experts, amounted to 8–10% in 2006. The highest returns - more than 12% per annum - are brought by bonds of third-tier issuers, but investments in them are associated with increased risk, which means a thorough preliminary analysis is necessary.
What is investment attractiveness
In order to determine the maximum efficiency of an investment decision, the concept of investment attractiveness of an enterprise has been introduced. The concept is quite new; it appeared in economic publications relatively recently and is used mainly in the characterization and assessment of investment objects, rating comparisons, and comparative analysis of processes. The study of various points of view on its interpretation made it possible to establish that in modern ideas there is no single approach to the essence of this economic category.
One of the most common points of view is the comparison of investment attractiveness with the feasibility of investing in an enterprise of interest to the investor, which depends on a number of factors characterizing the activity of the entity. The definition, although correct, is quite vague and does not provide grounds for discussing the assessment.
More precisely economic entity investment attractiveness is given in the definition by L. Valinurova and O. Kazakova. They understand by this term totality objective signs, properties, means and opportunities that determine potential effective demand for investment. This definition is broader and allows taking into account the interests of any participant in the investment process.
There are other points of view (including L. Gilyarovskaya, V. Vlasova and E. Krylov and others). Here, investment attractiveness is understood as an assessment of the efficiency of using equity and borrowed capital, an analysis of solvency and liquidity (a similar definition is the structure of equity and borrowed capital and its placement between different types of property, as well as the efficiency of their use).
Assessing investment attractiveness from the point of view of income and risk, it can be argued that this is the presence of income ( economic effect) from investing funds with a minimum level of risk.
The role of this concept in characterizing the investment environment and investment activity in general can be seen in the following diagram:

Thus, it becomes obvious that, regardless of the approach to definition used by an expert or analyst, most often the term “investment attractiveness” is used to assess the feasibility of investing in a particular object, choosing alternative options and determining the efficiency of resource allocation.
It should be noted that determining investment attractiveness is aimed at generating objective, targeted information for making an investment decision. Therefore, when approaching its assessment, one should distinguish between the terms “level economic development" and "investment attractiveness". If the first determines the level of development of the object, the set economic indicators, then investment attractiveness is characterized by the condition of the object, its further development, prospects for profitability and growth.
Assessment methods
The formation of a methodology for assessing the investment attractiveness of enterprises in Russia is at an early stage. This can be judged not only by the small number of publications on this problem, but also by the almost complete absence of specific working methods.
One of the most common is the analysis of investment attractiveness based on a single analytical indicator of the level of profitability of own assets. This approach, apparently, can take place for sampling the organization’s policies, determining the most effective ways to use capital in the investment process, and forming certain areas of investment activity. Since it requires studying a minimum set of factors influencing decision-making, its advantage is relative efficiency, especially if there is a large amount of information on homogeneous investment objects. At the same time, almost any investment object can be assessed. But this approach also has noticeable disadvantages - first of all, the high probability of inaccurate assessment, the inability to compare the results of the analysis due to the lack of a single information base, forming indicators. An individual approach to evaluating investment objects also has an impact. In essence, the process in this case comes down to a subjective assessment of a specific object by one or another investor, which in turn increases both the time and cost costs of conducting the analysis, and in addition, significantly complicates the identification of the required parameters, criteria and main factors on influencing her. It is also known that many companies sometimes deliberately overestimate current costs, which means that real data on profitability are distorted and, accordingly, the efficiency indicator decreases.
In practice, assessing investment attractiveness often comes down to analysis financial condition proposed investment targets. This approach not only theoretical basis, but the practical effect. The degree of complexity and complexity of the analysis depends on who is conducting it. However, as clear example We present criteria for assessing the investment attractiveness of the issuer of bills of exchange, which are used by a number of analytical services.

This kind of calculation is a condensed form of financial analysis, which allows an investor to quickly determine the advisability of further consideration of a particular enterprise as a potential investment object. However, such an analysis (as well as a detailed financial analysis) allows you to evaluate only the current financial situation enterprise, but at the same time does not answer a number of extremely important questions for the investor.
- What are the factors of investment attractiveness of an enterprise?
- What is the current market value enterprises?
- What is the magnitude of future cash flows from current investments?
Answering such questions is extremely difficult; this requires the development of complex, integrated techniques. For example, when assessing factors of investment attractiveness, an investor should pay attention to the following points:
- level of professionalism of the management team;
- the presence or absence of a unique business concept, a clear understanding of the company’s development strategy, and a detailed business plan;
- the presence or absence of competitive advantages, i.e. potential for market leadership;
- the presence or absence of significant potential to increase the company's revenues;
- the degree of financial transparency, compliance with corporate governance principles, or the company's commitment to transparency;
- characteristics of the ownership structure that ensures the protection of share capital;
- the presence or absence of the potential to obtain high returns on invested capital.
And this is only a small part of what needs to be found out. In order to reliably and effectively assess investment attractiveness, the list of factors will have to be significantly expanded - it should cover all areas of the enterprise’s activities.
Expert assessment is most effective in such cases, but today this is an infrequent phenomenon. Meanwhile, it is precisely this that should become an integral part of a comprehensive assessment of the investment attractiveness of an enterprise.
Answers to the last two questions - about current market value and future cash flows - are quite difficult to obtain. But it is necessary, since it is the current market value of an enterprise that allows us to characterize its possible growth potential, and therefore the possibility of generating income in the future.
In the future, the methodology for assessing investment attractiveness will be significantly expanded and supplemented. The simplest financial analysis no longer meets the requirements of investors making decisions. In accordance with this, new methods and approaches are being developed to determine the investment attractiveness of an enterprise and formulate an investment decision. In particular, it is planned to develop a set of assessment measures, which, in addition to financial analysis, will include a qualitative and quantitative assessment of factors of investment attractiveness and use several approaches to business assessment in order to determine cash flows in the future.
1 Basic numerical data are presented in RCB No. 3 (330), 2007.
2 RCB No. 3 (330), 2007.
There are different investors in the market: international, foreign, domestic, intra-corporate. And the level of investment also differs in scale and focus. Let’s imagine the image of a professional direct investor, say a foreign one. The investor has assets and intends to invest them profitably. He has carefully studied the investment climate of our country, regions and industries in which he has some experience in management and success. Finally, the direct investor sees in front of him a list of enterprises that interest him. In other words, the investment attractiveness of the company. How to perceive, evaluate and use it? We will devote this article to these questions.
Correlation between life cycle stages and company attractiveness
Investment attractiveness enterprise is truly an important step in the activities of professional investors interested in effective investments. The attractiveness of a company as an investment object is the result of a set of diagnostic and assessment measures carried out after selecting companies for the long list of industry interests of analysts. Every investor asks himself what criteria of investment attractiveness he should apply in order not to make a mistake in choosing an object. First of all, you should pay attention to the current stage life cycle companies as a diagnostic criterion.
A well-known authority on the theory of the life cycle (LC) of a corporation, Dr. Itzhak Calderon Adizes observes two large phases in the life cycle: growth and aging. We are more interested in such stages as “courtship-birth”, “infancy-childhood”, “adolescence”, “early blossoming” and “late blossoming” in the growth phase. Stages of aging: “decline”, “aristocratism”, etc. are of interest to a significantly lesser extent, since investing at this phase is already less attractive, unless the stages of “decline” or “aristocratism” precede the beginning of a new, more powerful cycle with the accompanying organizational and technological re-equipment of the business.

Life cycle stages according to I.K. Adizes
The subject for understanding possible investments can be any of the stages of the growth phase, however, the stages of “Come on, Come on”, “Youth” and “Flourishing” are still preferable. The “Infancy” stage is very risky for investments, since it is not yet clear how events will develop. At the stabilization stage, the investor must make sure that the enterprise will ensure high rates of production and sales of products while maintaining high margins of the main group of products and services.
How to determine the current stage of a company's life cycle? There are various techniques for this. First of all, you should collect performance indicators of the enterprise, preferably within five recent years with a quarterly breakdown and analyze their dynamics using the following analytical sections:
- volume of product sales;
- currency of the balance sheet asset;
- size equity companies;
- the size of EBIT, EBITDA, net retained earnings.
Assessing the attractiveness of a business based on SOFIA and life cycle stages
It is advisable to begin an analysis of the investment attractiveness of an organization based on the life cycle factor with a financial analytical study using the SOFIA method. The method involves research into ways of adopting basic financial decisions. Assessment of strategic decision making (or “S” type decisions) includes activities that simultaneously present methods for assessing investment attractiveness. They include the following analytical sections.
- Economic value added EVA. If the EVA value systematically shows positive dynamics, this means that the market value of the enterprise increases above the book value of net assets. Consequently, the investment attractiveness of the company is high.
- The market value of the company, determined using one of the available methods. For the investor, the income method (from the point of view of the possible sale of the business) and valuation by analogy are preferable.
- Models of sustainable growth (development) BCG. This method involves analyzing the correspondence of the identities of growth rates and increases in revenue, profit, assets, equity and debts of the enterprise. The most pronounced and synchronous dynamics of indicators are characteristic of the “Youth” and “Early Bloom” stages, which makes them especially attractive for investment.
- Matrices of financial strategic models. The chosen financial strategy of the company serves as an indirect pointer to the investor to the formed trend, how successfully the direction has been chosen in the two-factor matrix of economic and financial activities. The success zone refers to the direction towards the creation of liquid funds, and the deficit zone refers to their consumption.
- Dupont model. This analytical model is more than a hundred years old. There are two-factor and three-factor DuPont models. They are based on a detailed analysis of the company's return on assets.
Factors of investment attractiveness are present not only in the company’s chosen financial strategy. Of no small importance is current system operational financial planning (type “O” decisions). The area of regular management in the field of finance is no less important for an investor who is contemplating a business for investment. By this we mean a budget management system and a rationing system.
Assessment of the investment attractiveness of an enterprise is based on an analysis of a set of existing policies in the field of accounting, cost management, working capital And accounts receivable(decisions of type “F”), investment policy of the enterprise (decisions of type “I”). The actual level of development of analytical technologies in financial sector also serves as a certain “beacon” of investment security (type “A” decisions).
Established architecture financial management company using the SOFIA method allows you to determine the stage of the life cycle and obtain comprehensive information on the profitability and prospects of investments. In addition to the financial aspect, diagnostics of organizational behavior in the enterprise are also useful for understanding the moment of development of the company. The relationship between types of management practices and life cycle stages is presented below in tabular form.

Diagnosis of the life cycle stage through types of management practices in the company
Focused financial analysis to assess attractiveness
The investment attractiveness of a business object is assessed during several iterations from different points of view. It is necessary for both sides of the negotiation evaluation process to understand that only a certain openness, subject to the conditions of information security, can lead to mutual success in raising funds. The investor must prove to the owners and management of the company that, acting in its business interests, it does not pose a competitive threat. The initiator of the investment on the part of the company must realize that it will be necessary to open the main aspects of the operating results and the management system.
Indicators of profitability, liquidity, financial stability, asset turnover serve as the basis for a focused analysis of the enterprise as a potential investment object. Based on these indicators, the investment attractiveness of the enterprise is assessed from the position of investment opportunities for investments in fixed assets or portfolio investments. The following presents the composition of the indicators used in the analysis, summarized in three groups.

Summary table of indicators for analyzing investment attractiveness
An analysis of the investment attractiveness of an enterprise can be carried out by comparing the calculated values with the standard (normative) level of the indicator on average for the industry, with the level of previous reporting periods of the given company and with the found values of the leading competitors in the industry and in the territory. The analysis will require the results of competitive intelligence, information from central and regional branches Rosstat (based on industry average indicators) and reporting forms past periods for the enterprise.
The investment attractiveness of an enterprise according to the first group of indicators allows an investment analyst to determine the potential for investor protection from demands external obligations, thanks to resources own funds. The second group shows the company’s ability to cover short-term liabilities through a short and liquid asset base. In this case, the overall coverage ratio is optimal within the indicator value of 2-2.5, and the intermediate ratio is at the level of 0.8.
The most liquid part of assets is cash. Taking into account this circumstance, the coefficient absolute liquidity are of particular importance to both investors and suppliers. The most favorable option is considered when this indicator exceeds the value of 0.5, and its optimal value is 0.25. Various types profitability serve as a separate analytical unit for assessing the attractiveness of the company. Standard values vary greatly across industries and depend on seasonality and, as already noted, on the stage of the life cycle.
The influence of management level on the degree of investment attractiveness
Quite often, a potential investor is interested not only in the level of the company as a whole. Investment analysts may also be interested in the investment attractiveness of the project as a local investment task. The previous sections emphasized financial analysis as a key tool in the selection of objects for capital investment. This is truly the most effective way to solve the search and selection problem. Figures, provided they are open and reliable, provide direct access to a forecast for the success of an investment.
At the same time, financial analytics must be confirmed by indirect techniques and methods, without which the assessment of the investment attractiveness of an enterprise and local projects is not entirely complete. In addition to the above diagnostics of organizational behavior in a company, it is advisable to clarify the type of current organizational culture. It, to one degree or another, indicates the stage of life cycle and the level of development of management in the company, and reflects the current management paradigm.
The reliability and competitiveness of the company as an investment object is confirmed by the level of development of management systems based on quality management. ISO standards of various series, starting from 9000, are considered in many countries as one of the most effective indirect assessment tools. The very fact of certification according to quality standards increases the attractiveness of a company in terms of investment opportunities due to:
- a transparent and prescribed model of regulated business processes in the company, which gives the investor support in the subsequent control of procedural well-being;
- implementation electronic forms documentation support for management;
- obtaining opportunities to enter international markets on the basis of clear and generally accepted procedures and standards;
- clear language and format for internal corporate communications, plans and reporting accepted by both company employees and investor representatives;
- production costs, which receive an optimization perspective along with process optimization procedures through functional cost analysis and business process reengineering.
As a summary
There are at least two parties involved in the investment process. One party, giving money for capital investments, is called an investor and expects a corresponding return. The second party initiates an investment project and needs to back it up with funds if its own capital is insufficient. She is called the initiator of attracting an investor. Not only must both parties find each other somehow, but mutual choice is highly desirable in a win-win disposition. Unfortunately, the national pastime of Russian business consists of performing rituals that lead to losses.
I understand investors why there are so few of them and why the cost is inflated investment funds for companies. The reason for this lies not only in the fact that the business is truly unprofitable and ineffective. In fact, there are not so few successful companies in the economy. It's all about three important aspects.
- The initiating companies first do not want, and only then “do not know how” to be transparent to potential investors.
- Regulated management is often truly shell-like, imitative and formal in nature, including TQM and ISO certificates.
- Investors need to learn how to persuade, analyze and evaluate the investment potential of truly attractive businesses.
Sometimes it seems that the investment attractiveness of an enterprise, as well as its composition true values fundamental indicators of its activities are hidden not only from the eyes of investors, but also from the business owners themselves. It’s time to stop double standards in economics a long time ago. The most interesting thing is that monopolies and oligopolies as entities also suffer from the fact that medium and small businesses are shackled in the murk of tax maneuvering. This is as much a matter of state sovereignty as national security. For some reason, it is believed that the foundation will be broken, and the quality and volume of investments in the real sector will gain new strength.
Investment attractiveness
1. The concept of investment attractiveness and its components
2. Methods for determining investment attractiveness
3. Investment attractiveness of economic sectors
4. Investment attractiveness of enterprises
The processes of regional development in modern Russia determine the degree of investment attractiveness of the region for domestic and foreign potential investors. Investors' interest in investing in projects on the territory of the Russian Federation is directly related to the level of development of various subsystems of the regional economy. An investor's choice of location for a particular property depends on many factors. Their correct and objective assessment determines the effectiveness of the implementation and operation of the project at all stages of its life cycle. Without formalized analytical tools in their arsenal to assess the situation in the regions where an object could potentially be located, investors often make decisions about the location of its implementation based on a subjective perception of the investment attractiveness of a particular region.
On modern stage development, it is necessary to take into account global trends in deepening the integration of national and regional economies, the free movement of investment capital and, as a consequence, the interest of potential investors in the implementation of various projects in the Russian Federation. Currently, there is a need for detailed, well-structured information about the economic, financial, socio-political state of the regions of the Russian Federation, which could be used by potential investors. Obviously, this information must be obtained from reliable sources, assessed using modern analytical methods and models, and presented in a form convenient for the potential consumer.
In the economic literature, such concepts as “investment climate” and “investment attractiveness” are very often identified.” We cannot agree with this, because... The investment climate includes both investment attractiveness and investment activity, determined by the volume of capital investments per capita of the region, the rate of change in investment volumes, etc.
The investment climate includes the objective capabilities of a country or region (investment potential) and the conditions for investor activity (investment risk). Investment potential is the sum of objective prerequisites for investment, depending both on the availability and diversity of areas and objects of investment, and on economic “health”. Regional investment climate is a system of socio-economic relations that are formed under the influence of a wide range of interrelated processes at the macro-, micro- and the regional levels of management and create the preconditions for the emergence of sustainable investment motivations.
Investment attractiveness- this is a set of factors favorable for investment that characterize the investment climate of the region and distinguish this region from others.
The investment attractiveness (climate) of a region is determined by investment potential and investment risk.
Investment potential of the region- These are the region’s potential for economic development. Investment potential takes into account the readiness of the region to receive investments with appropriate guarantees of capital safety and profit for investors. It includes the following components, i.e. private potentials:
Resource and raw materials (weighted average provision of balance reserves of the main types of natural resources);
Labor ( labor resources and their educational level);
Manufacturing (gross regional product);
Innovative (the level of development of fundamental, university and applied science with an emphasis on the implementation of its results in the region);
Institutional (degree of development of market economy institutions);
Infrastructure (economic and geographical position of the region and its infrastructure provision);
Financial (volume tax base and profitability of regional enterprises);
Consumer (total purchasing power of the region's population).
Investment risk- this is the probability (possibility) of loss of capital.
Investment risk is calculated based on the following components:
Economic risk (trends in the economic development of the region);
Financial risk (the degree of balance of the regional budget and the finances of the enterprise);
Political risk (distribution of political sympathies of the population based on the results of the last parliamentary elections, the authority of local authorities);
Social risk (level of social tension);
Environmental risk (level of environmental pollution, including radiation);
Criminal risk (crime level in the region taking into account the severity of crimes);
Legislative risk (legal conditions for investing in certain areas or industries, the procedure for using individual factors of production). When calculating this risk, a combination of federal and regional laws and regulations regarding investments is used.
Inaccuracies in the analysis of the integral potential and integral risk of regions using this methodology are mainly associated with the determination of the weights (shares) of the components of potential and risk.
The authors of the methodology assigned the greatest weight to consumer, labor, production potentials, legislative, political and economic risks, and the least weight to natural resource, financial and institutional potentials, and environmental risk.
Investors attach special importance (as surveys have shown) to labor and consumer potential, i.e. they are primarily interested in the quality of local labor and the possibility of expanding production and salesgoods.Investors fear regional risksmoretotal legislative and political risks associated with each other.
The decision-making process on investing in a particular region is based on a detailed analysis of information about the investment attractiveness of this region and the state of its investment complex. Most leading foreign and domestic economic publications (Euromoney, Fortune, The Economist, Expert, etc.), as well as large consulting companies, regularly monitor information on the state of national and regional investment complexes. On its basis, ratings of investment attractiveness of national economies and regions are published. A variety of methods are offered for compiling such ratings.
As initial information for compiling ratings of investment attractiveness, statistical data on regional development, legislative acts related to the regulation of investment activities, results of regional studies and surveys, and press publications are used.
When compiling almost all ratings, expert assessments are used to one degree or another. Domestic and foreign experts are involved in forming a set of indicators by which the investment attractiveness of the region will be assessed and assessing the weights of these indicators in the resulting integrated assessment.
1. A set of indicators is selected and justified, most accurately, in the opinion of experts, reflecting the state of the investment complex of the region.
2. Each indicator or group of homogeneous indicators is assigned weights corresponding to its (their) contribution to the investment attractiveness of the region.
3. An integral assessment of investment attractiveness for each region is calculated.
Let's consider some well-known methods for assessing the investment attractiveness of regions of the Russian Federation, developed by domestic and foreign experts: the methodology of the consulting agency "Expert" (Fig. 1) and the methodology of the Economic Department of the Bank of Austria. (Fig. 2).
It is worth noting that both methods require the formation of a constant set of indicators and regular calculation on its basis of an integral assessment characterizing the state of the investment climate of the regions and their attractiveness for potential investors. Their advantage lies in the ability to trace the dynamics of economic, social and other regional processes based on a constant set of criteria. Well-known rating agencies use this method, and in some cases it can be said that using the same set of assessment criteria from year to year is justified, because Over time, such ratings become universal indicators when assessing the state of the economies of states and regional entities. An obvious difficulty is the selection and justification of the effectiveness of using a specific set of evaluation criteria. It is also difficult to interpret the results obtained from the assessment. It is not always possible to see cause-and-effect relationships and development trends of the regional investment complex behind the final integral value.
A distinctive feature of the methods is that they all use grouping of assessment indicators according to investment potentials and risks. The main problem when using them is the difficulty of forming and justifying a set of assessment factors.
In our opinion, the general limitations of existing methods for assessing the investment attractiveness of regions of the Russian Federation is their excessive “rigidity”. An expert using one or another method does not have the opportunity to introduce into the assessment procedure new and/or exclusions proposed by the developer, factors or groups of factors. The developers also limit the user to standard calculation procedures.
As can be seen from the above diagrams, the results of rating assessments are presented in different ways.
In the case of the Expert agency’s research, the result of the work was a matrix of distribution of Russian regions according to investment conditions, where classification was introduced vertically according to the level of investment risk, and horizontally - according to investment potential. In accordance with the agency’s methodology, all regions are divided into 12 groups.
|
maximum |
reduced |
minor |
||||
|
moderate |
||||||
|
minimum |
||||||
|
extreme |
In accordance with the methodology of the Economic Department of the Bank of Austria, each region receives three ratings:
2. The region’s place in the Russian Federation in accordance with the obtained assessment of investment attractiveness.
3. Determination of the investment situation in the region as belonging to one of 6 classes.


The main goal of studying the investment attractiveness of economic sectors is to ensure the diversification of their activities, especially in the field of real investment. For an investor making an investment decision, it is important to determine in which industry a specific investment project can be implemented with the greatest efficiency, which areas of investment will have the best prospects and will provide a high return on invested capital.
Assessing and forecasting the investment attractiveness of economic sectors is carried out using the same methods and in the same sequence as at the macroeconomic level (monitoring a system of informative indicators; constructing a system of analytical indicators, their analysis and evaluation; forecasting investment attractiveness).
When assessing and forecasting the investment attractiveness of economic sectors, it is important to take into account the role of individual industries in the country’s economy, the prospects and efficiency of their development, the degree of government support for this development, the level of investment risks characteristic of various industries, and other synthetic (generalizing) indicators. Each of the synthetic indicators is assessed based on the totality of its analytical components, the calculation of which is based on statistical data and forecast estimates.
When assessing the level of efficiency of the industry, the following can be taken as an analytical indicator: level of profitability of assets used. It is calculated as the ratio of profit from sales of products (or balance sheet profit) to the total amount of assets used. Besides, the inflation factor, the policy of taxation of products and profits, the level of costs, selling prices for products and other factors must be taken into account.
The prospects for the development of the industry as one of the most important criteria for assessing investment attractiveness are studied on the basis indicators of profitability and risk, directions, rates and forms of privatization, assessment of the level of export potential of products and the level of their price protection from imports, inflation protection of manufactured products, etc..
The level of industry development prospects is assessed using the following analytical indicators:
The importance of the industry in the economy (actual and projected shares of products in GDP, taking into account the structural restructuring of the economy);
Industry resistance to economic recession in the economy as a whole (indicators of the ratio of the dynamics of the industry's production volume and the country's GDP);
Social significance of the industry (indicator of the number of employed workers);
Securing growth prospects with own financial resources (volume and specific gravity capital investments at the expense of the industry’s own funds, the share of equity capital in the assets used).
In the process of assessing and forecasting the investment attractiveness of industries, it is important to take them into account life cycle consisting of 5 phases:
1. Birth phase characterizes the development and implementation of fundamentally new types of goods and services, the need for which causes the construction of new enterprises, which later constitute an independent sub-industry, and then an industry. This phase is characterized by significant volumes of investment, minimal profits and the absence of dividend payments on shares.
2. Growth phase associated with consumer recognition of new types of goods and rapid growth in demand for them. During this phase, investment is carried out at a high rate, the company's profits grow, shares are issued, and dividends are often paid in the form of additional shares.
3. Expansion phase is the period between high growth rates in the number of new enterprises in an industry and stabilization of this growth. At this stage, investment in new construction continues, but the bulk of investment is directed toward expanding existing production facilities, the growth in the number of new enterprises is stabilized, the issuance of new shares continues, and the payment of dividends in cash begins. However, the main direction in dividend policy during this period involves the payment of dividends in the form of additional shares and the splitting of existing shares.
4. Maturity phase determines the period of greatest demand for industry goods, improving the quality characteristics of products. The main volume of investments is directed to the modernization of equipment and technical re-equipment of production. This is one of the longest stages of the industry life cycle. For goods of constant demand that are not influenced by scientific and technological progress, the maturity phase is the last in the life cycle (for example, agricultural production, raw materials industries, etc.). Enterprises in industries in the maturity phase receive maximum profits and pay high dividends in cash.
5. Decline phase completes the life cycle of an industry and characterizes a period of sharp decline in demand for products due to the development of new industries, the products of which replace obsolete ones. Typically, this stage is typical for industries whose products are largely influenced by scientific and technological progress.
The change in the stages of the life cycle of industries is associated mainly with the policy of structural restructuring of the economy, aimed at introducing the latest achievements of science and technology, ensuring the competitiveness of domestic production on the world market, increasing the balance of the economy, accelerating the development of industries that increase export potential, increasing the social orientation of production, and reducing energy intensity , development of intersectoral cooperation, etc.
The end result of assessing and forecasting the investment attractiveness of industries is their grouping and ranking according to the degree of their attractiveness.
The final stage of studying the investment market is the analysis and assessment of the investment attractiveness of enterprises as potential investment targets. Such an assessment is carried out by the investor to determine the feasibility of capital investments in new construction, expansion, reconstruction or technical re-equipment of existing enterprises, selection of alternative privatization objects, search for acceptable investment projects in the real estate sector, purchase of shares of individual enterprises, etc.
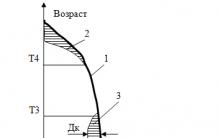
The development of the enterprise takes place sequentially in time in a combination of cycles of various products of its activity. This Cycle can be divided into periods with different turnovers and profits: childhood (small increase in turnover, negative financial results); youth (rapid growth in turnover, first profit); maturity (slower turnover growth, maximum profit); old age (turnover and profits fall). The general life cycle of an enterprise is determined to be approximately 20-25 years, after which it ceases to exist or is reborn on a new basis with a new set of owners and managers.
The concept of the life cycle of an enterprise allows us to identify various problems that arise during its development and evaluate its investment attractiveness.
During childhood The enterprise faces mainly survival problems in the form of cash flow difficulties, when it is necessary to find short-term means of financing, as well as sources of investment for future development. During my youth the first profit allows the enterprise to reorient itself from profitability to economic growth. Now to maintain economic growth it needs medium- and long-term sources. During maturity The company tries to extract maximum profit from its production, technical and commercial potential. The ability to self-finance is quite significant. Given the aging of goods, enterprise managers must find new development opportunities through industrial investment or financial participation, for example in the activities of another enterprise. In this case, there is a gradual transformation of the enterprise into a holding company, i.e. V financial enterprise portfolio management securities.
Enterprises in the process of growth in the first two stages of their life cycle are considered the most attractive for investment. Enterprises in the maturity stage are also attractive for investment in the early periods, until the highest point of economic growth is reached. In the future, investment is advisable if the company’s products have fairly high marketing prospects, and the volume of investments in modernization and technical re-equipment is relatively small and the invested funds can pay off in the shortest possible time. At the stages of old age, investing, as a rule, is not advisable, except in cases where large-scale diversification of products or re-profiling of the enterprise is planned. At the same time, some savings in investment resources are possible compared to new construction.
The stage of an enterprise's life cycle is determined as a result of a dynamic analysis of indicators of production volume, total assets, equity capital and profit for a number of recent years. By the rate of their change one can judge the stage of the enterprise’s life cycle. The highest rates of growth in indicators are characteristic of the stages of adolescence and early adulthood. Stabilization of indicators occurs at the stage of final maturity, and a decrease - at the stage of old age.
Assessing the investment attractiveness of enterprises also involves conducting a financial analysis of their activities. Its purpose is to assess the expected profitability of invested funds, the timing of their return, as well as to identify the most significant investment risks in terms of financial consequences.
An assessment of the financial performance of an enterprise is carried out in the process of analyzing a system of interrelated indicators that characterize the effectiveness of financial activities from the point of view of compliance with the strategic goals of the business, including investment ones. The most important results characterizing the unity of tactical and strategic goals for the development of an enterprise are revealed by analyzing asset turnover, profitability of capital, financial stability and liquidity of assets.
Investment attractiveness is not only a financial and economic indicator, but a model of quantitative and qualitative indicators - assessments of the external environment (political, economic, social, legal) and the internal positioning of an object in the external environment, a qualitative assessment of its financial and technical potential, which allows you to vary the final result.
In modern economic literature there is practically no clarity in defining the essence of investment attractiveness and the correct system for its assessment. So, Glazunov V.I. argues that the assessment of investment attractiveness should answer the question of where, when and how many resources an investor can direct in the process of making investments. Rusak N.A. and Rusak V.A. they reduce the determination of the investment attractiveness of an object mainly to heuristic methods associated with ranking the objects under study based on the assessment of specialists (experts). Hence, investment attractiveness concerns the comparison of several objects in order to determine the best, worst, average.
Many experts equate investment attractiveness to assessing the effectiveness of investment projects.
The investment attractiveness of an enterprise is a certain set of characteristics of its production, as well as commercial, financial, and to some extent management activities and the characteristics of a particular investment climate, the results of which indicate the feasibility and necessity of investing in it. As a rule, the winner is an investment-attractive object in which investments are made.
So, the primary task, the implementation of which predetermines success in this very difficult competition, is the maximum qualitative increase in investment attractiveness.
The first step in solving this problem will be to determine the necessary parameters existing level investment attractiveness within a particular object. That is, there is a need for a high-quality and qualified assessment of multi-level investment attractiveness, namely: international, domestic, sectoral, inter-industry, intra-industry, specific enterprise, project.
The main goals of assessing investment attractiveness are:
Determination of the current state of the enterprise and prospects for its development;
Development of measures to significantly increase investment attractiveness;
Attracting investments within the framework of appropriate investment attractiveness and volumes of obtaining an integrated approach for a positive effect from the development of attracted capital.
The final stage in the process of studying the investment market is a qualitative analysis and objective assessment of investment attractiveness for individual companies and firms considered as potential investment targets.
This range of assessments is carried out by the investor when determining the need and feasibility of capital investments in the process of expansion and technical re-equipment at existing enterprises; selection for the acquisition of alternative privatization objects; as well as when purchasing shares of individual companies. But each economic entity must demonstrate its capabilities to attract external investment. Therefore, the assessment of investment attractiveness is analyzed in external and internal financial analysis.
Analysis of investment attractiveness assessment
Western economists have determined that in order to assess the investment attractiveness of an enterprise as an investment object, the most important and priority is a complete analysis of the following vital aspects of its activities:
1.Analysis of asset turnover. The effectiveness of starting an investment is largely determined by the fact how quickly the invested funds manage to turn around in the course of the activities of a particular enterprise.
2. Analysis of return on capital. One of the main goals at the time of investment is mandatory security high profits in the process of using invested material resources. But in modern conditions, enterprises can largely control profitability indicators (due to depreciation policy, the effectiveness of tax planning, etc.), and in the context of the analysis process, it is possible to quite fully explore the potential of its formation in comparison with the initially invested capital.
3. Analysis of financial stability. Such an analysis makes it possible to assess the investment risk associated with the structural formation of investment resources, as well as to identify the optimal financing of current economic activities.
4. Analysis of asset liquidity. Assessing the liquidity of assets allows you to determine the ability of a particular enterprise to pay its short-term liabilities, prevent the possibility of bankruptcy through the rapid sale of certain types of assets. In other words, the state of assets characterizes the level of existing investment risks within a short-term period. Moreover, the assessment of the investment attractiveness of an enterprise according to the indicated indicators is carried out taking into account the stages of its life cycle, since at different stages the values of the same indicators have different values for the enterprise and its investors.
For the development of any organization, capital from external sources is required. interested in making a profit and increasing it. They take into account and try in every possible way to avoid losses and for this they evaluate the effectiveness of investing in an existing project.
Investment attractiveness of the enterprise
The investment attractiveness of an enterprise is a set of characteristics that show how effective it is to invest money in the further development of the enterprise. The predominant indicator is the factor of obtaining a stable income over a long period.
Today, many companies are in fierce competition to obtain additional capital for the development of a future project. Basically, they invest money in a project that is carefully designed; the investor can clearly see the picture of income after implementation. Therefore, it is worth developing a report with financial indicators, where you can see the nuances.
Assessment of the investment attractiveness of an enterprise is carried out by calculating the economic condition of the enterprise using financial indicators. These indicators include:
- liquidity - shows how quickly a company can turn its assets into cash when necessary;
- property status - reflects the share of current and non-current assets in common property enterprises;
- business activity - the indicator characterizes all financial processes in the enterprise, on which the profit of the enterprise in turn depends;
- financial dependence - shows the dependence of the enterprise on external sources of financing and whether it is possible to operate without additional funds;
- profitability - reflects the efficiency of the enterprise's use of its financial capabilities.
It is worth remembering that the assessment of investment attractiveness includes indicators of resource availability, product profitability, number of personnel, level of production capacity utilization, depreciation of fixed assets, availability of fixed and production assets, and others.
Methods for assessing the investment attractiveness of an enterprise
Economists argue that there is no single method for determining the investment attractiveness of an enterprise. Each project requires an individual method followed by an analysis of investment attractiveness. Assessment is possible using different methods, which are based on the use of suitable indicators and analyzed factors. This article carried out comparative analysis different types of assessment.

How to attract investors

If an enterprise needs additional funds, then management must take measures to increase the investment attractiveness of the enterprise.
There is practically no organization that does not need additional external capital. As is already known, investments help production grow, increase competitive advantages over other enterprises, profits increase, new technologies are introduced to improve production or. There are many advantages, but the main task lies in attracting funds.
There are a large number of ways to attract, but this does not mean the effectiveness of attraction. An ideal option would be to sell one business to open a new and potentially effective business.
First you need to sell existing option at the highest possible cost. The development of the future project depends on the sale. As practice shows, such investors are people who want to invest their money in a profitable business, some of them have extensive experience behind them. In such cases, profit maximization will most likely be observed.
In cases of global capital shortage, you can resort to direct investment. In turn, this method is divided into:
- investments from financial investors;
- strategic type of investment.
The essence of the first is the possibility for an investor to acquire a small part of the shares (but not a controlling interest) with subsequent sale after 2-5 years; it is also possible to place shares on the securities market, where there is a large circle of investors.
The investor's main income will come from selling shares, and in turn, the investment attractiveness of the organization will increase. This option will suit both the investor and the manager.
Strategic investing is based on the investor acquiring a large block of shares for a long time, where the investor becomes another of the owners of the company. The main goal of a strategic investor is to purchase an existing company or merge with his company. This option saves crisis situations, but this takes away the owner’s powers and the company becomes financially dependent on other sources of financing.
Investing in the form of borrowed funds
The company does not want interference in its management strangers, then in such a case there are bank loans, leasing, borrowing funds from legal and individuals.
 This investment policy of an enterprise is expressed using the example of modern business development, when entrepreneurs have a unique mindset, but do not have funds. In such cases, they resort to bank loan. In European countries, you can get a loan for business development at minimal interest rates, but in our country, on the contrary, they inflate the interest rate.
This investment policy of an enterprise is expressed using the example of modern business development, when entrepreneurs have a unique mindset, but do not have funds. In such cases, they resort to bank loan. In European countries, you can get a loan for business development at minimal interest rates, but in our country, on the contrary, they inflate the interest rate.
The terms of financing by investors range from one month to many years. In any case, the investor is interested in receiving interest from the use of his capital. The option is attractive and is available to many organizations, but the lender still requires fulfillment of obligations to pay interest and principal.
To increase the investment attractiveness of an enterprise, a number of measures can be taken:
- any enterprise that seeks to develop, first of all, is long term strategies, which can be used as a guide in the future;
- is definitely required, where the goals and ways to achieve profit maximization will be clearly expressed;
- there must be documentation of a legal examination in accordance with legislative norms;
- the company must create credit history(this is very easy to do by applying for a small loan from banking institutions and returning it in a short period of time);
- putting in order documents on the ownership of certain land plots and firms in general;
- ensure that the rights of shareholders and the powers of owners are spelled out in the charter documents of the enterprise;
After identifying and collecting the entire package of documents, it is worth paying great attention to the organization’s production process. Management personnel - chief technologist, engineer, sales manager, economist-analyst, HR manager - can handle this better. They are required to determine the strengths and weaknesses that prevent the enterprise from developing rationally, identifying and eliminating bottlenecks. It is necessary to carefully work with risks, determine the level of their threat, and find ways to weaken or eliminate them altogether.
Upon completion of all activities, it is required to show the investor that the enterprise has ways to improve the functioning of the enterprise.
In conclusion, we can say that the investment attractiveness of an enterprise depends on rational management. In order to obtain capital, maximum effort is required.










Carrying out an inventory
Ulyukaev, Navka and Patrushev
Income tax refund for treatment: registration procedure and calculation of the deduction amount
Import substitution - what is it?
OSAGO minimum insurance period