Often, a partial prepayment under an agreement providing for several deliveries or phased delivery of works is not credited as payment in full at the next delivery, but in parts as payment for several subsequent deliveries. For example, the contract provides for 10 deliveries. The price of each delivery is 1500 rubles. Prepayment - 1000 rubles. Of which, at each delivery of the goods, 100 rubles are credited to the payment account. And after each shipment, the buyer must pay an additional 1,400 rubles. Similar payment terms are sometimes prescribed when renting.
This payment procedure often ensures the interests of the seller in case the buyer does not pay for any of the next deliveries. Then the seller has the opportunity to set off the “unused" advance balance to repay the debt. In addition, such advances can be offset against not only payment, but also repayment of contractual sanctions.
How, in such cases, should the seller (contractor, landlord) be deductible, and the buyer (customer, tenant) can restore the advance VAT: the full amount at the first shipment or in parts as the contract is executed?
And sometimes the advance payment is entirely in payment of the last delivery under the contract (the last stage of work, last month rent). In this case, the advance payment remains in advance all the time until the last delivery (expiration of the last month of the lease, completion of the last stage of work). Should the parties defer the deduction and restoration of advance VAT until the full performance of the contract?
How does the seller accept upfront VAT deductible
Upon receipt of prepayment for its entire amount, you must accrue ND FROM sub. 2 p. 1 Article 167 of the Tax Code and in the next 5 calendar days, issue an advance invoice to the buyer at section 3, Art. 168 of the Tax Code.
At the first delivery you:
- add VAT to its value and issue a shipping invoice to the buyer at sub. 1 p. 1 Article 167, paragraph 3 of article 169 of the Tax Code;
- get the right to deduct the VAT calculated on advance payment and section 8, Art. 171, clause 6, Article 172 of the Tax Code. But how much VAT can be deductible if only part of the advance is credited to this delivery? And is it possible to declare a deduction now, if the advance payment for this delivery is not counted at all, but is used to pay for the next deliveries?
The rules are formulated in the Tax Code of the Russian Federation very succinctly. It says only that tax amounts calculated from advance payments are deductible from the date of shipment relevant goods (works, services) )section 8, Art. 171, clause 6, Article 172 of the Tax Code.
Thus, for deduction at the first delivery, you can only accept VAT from the amount of the advance payment that corresponds to the goods shipped. How to establish correspondence between advance payment and shipment? You have two options:
- <или> under the terms of the contract;
- <или> at the cost of goods shipped.
OPTION 1. Accept VAT deduction based on the terms of the advance credit agreement
For example, if only 100 rubles are credited to one shipment. from the advance payment paid in the amount of 1000 rubles, then for deduction we accept only VAT from 100 rubles. And we will deduct VAT from the rest of the advance payment as we deliver those parties in payment of which it is credited. If, under the terms of the contract, the entire amount of the prepayment is used to pay for the last delivery, then until the day of the last shipment we do not deduct anything.
Indirectly, this conclusion also follows from the Letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia, in which it indicated that “the determining condition for accepting for deduction of tax previously paid to the budget from advances received is the fact of offsetting the advance on account of the shipment of goods (work performed, services rendered) » .
Example. Deduction of advance VAT from seller at option 1
/ condition / Work worth 3,540,000 rubles. (including VAT 540,000 rubles) are carried out in two stages. An advance payment of 40% of the cost of the work, that is 1,416,000 rubles. (3,540,000 rubles. X 40%), including VAT 216,000 rubles., The customer makes in the I quarter of 2011
30% of the advance payment (this is 424,800 rubles, including VAT of 64,800 rubles) is credited against the payment of the first stage of work, and 70% (this is 991,200 rubles, including VAT of 151,200 rubles) - against payment of the second.
The cost of the first stage is 1,534,000 rubles. (including VAT 234,000 rubles). The stage was commissioned in the II quarter of 2011. The cost of the second stage is 2,006,000 rubles. (including VAT 306,000 rubles). The deadline for the completion of the stage is the fourth quarter of 2011.
/ decision / For deduction in the II quarter, the contractor will declare only part of the advance VAT - 64,800 rubles. (from 424 800 rubles in advance, credited as payment for the first stage). The remainder of the advance VAT is 151,200 rubles. - the contractor deducts in the IV quarter, when he passes the result of the second stage of work.
In repayment of his debt for the payment of the first stage, the customer must transfer 1 109 200 rubles. (1,534,000 rubles - 424,800 rubles). And the rest of the advance payment in the amount of 991,200 rubles. (1,416,000 rubles - 424,800 rubles) will be set off against the second stage of work.
OPTION 2. Accept VAT deduction in the amount indicated in the shipping invoice
Such an approach can be justified by the fact that the Tax Code does not directly indicate the need to take into account the terms of the advance set-off agreement.
Compare the advance amount and the cost of the first delivery:
- <если> the advance amount is less, then we deduct the entire amount of the advance VAT;
- <если> the amount of the advance is greater, then we deduct the advance VAT in deduction in an amount equal to that indicated in the invoice for shipment. The VAT on the balance of the advance according to the same algorithm is deductible for the next deliveries under this agreement.
Example. Deduction of advance VAT from seller at option 2
/ condition /
/ decision / The contractor compares the cost of the first stage - 1,534,000 rubles. (including VAT 234,000 rubles) - and the amount of the advance payment - 1,416,000 rubles. (including VAT 216,000 rubles). The advance amount is less, which means in the second quarter (upon delivery of the results of the first stage), the entire VAT calculated from the advance payment should be deducted, that is, 216,000 rubles.
In repayment of his debt for the payment of the first stage, the customer in the III quarter transferred 1 109 200 rubles. (1,534,000 rubles - 424,800 rubles).
Meanwhile, the cost of the first stage minus the full amount of the advance payment is 118,000 rubles. (1,534,000 rubles - 1,416,000 rubles).
The difference between these two amounts is 991,200 rubles. (1 109 200 rub. - 118 000 rub.). Its executor must recognize the advance payment of the remaining stages received in the III quarter, accrue VAT of 151,200 rubles on it. (991,200 rubles. X 18/118) and issue an advance invoice to the customer.

This option is risky. In one of the letters, the Ministry of Finance indicated that VAT on prepayments, on account of which goods in a particular quarter were not shipped, are not deductible in this quarter t Letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 02.25.2009 No. 03-07-10 / 04. And, based on this statement, the tax authorities are likely to recognize as unlawful the deduction of VAT on the balance of the advance payment not credited to the current supply. Then they will charge you tax, charge interest and, possibly, a fine for non-payment of tax under Art. 122 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
However, inspectors should not have complaints if the buyer finally settles for the first delivery in the same quarter in which it took place.
After all, it will turn out like this: first, you will accept the deduction of VAT from the advance in the amount of “shipping” tax or in the amount of the advance (depending on which amount is larger). Then, upon receipt of payment for the current delivery, an overpayment will occur, which you should consider as an advance payment for VAT purposes. It will be equal to the amount of the initial advance payment and received from the buyer as the final calculation for the first delivery of payment minus its contractual value (in our example, 991,200 rubles will have to be recognized as an advance for VAT purposes). Again it is necessary to accrue an advance tax. You also need to issue an advance invoice to the buyer for this amount. And at the end of the quarter, deduction and accrual advance tax close each other. That is, you will not have any benefit.
OUTPUT
As you can see, option 2 is more profitable for you if the buyer pays for the delivery not in the shipment quarter. However, the tax risks associated with this option are great.
How can a buyer restore advance VAT
After transferring the prepayment and receiving an advance invoice from the seller, you have the right to declare the advance payment indicated therein for deduction VAT section 12, Art. 171, clause 9, article 172 of the Tax Code. Then, after taking the first batch of shipped goods for accounting and receiving a shipping invoice, you have:
- the right to deduct the shipping document indicated therein FROM clause 1, Article 172 of the Tax Code;
- obligation to restore an advance ND previously accepted for deduction FROM sub. 3 p. 3 Art. 170 of the Tax Code. But how: all at once, or only in that part, which is credited as payment for this delivery?
The Tax Code of the Russian Federation only indicates that the amount of VAT in the amount previously accepted for deduction in respect of prepayment should be restored in the period in which the tax on the purchased goods (work, services) is deductible )sub. 3 p. 3 Art. 170 of the Tax Code.
If you literally read this rule, you might think that for any delivery following an advance, you need to restore the entire deduction - not taking into account either the purchase price or the terms of the contract. But, fortunately, this is not so. Above we quoted a letter from the Federal Tax Service of Russia, from which it follows that for the deduction of VAT from the advance payment from the seller it is important how much of this advance is set off against the shipment. It substantiated this by the FTS with the principle of mirroring, which suggests indirect tax. This principle allows the buyer to restore only that part of the advance VAT previously accepted for deduction, which falls on the cost of the goods received and Letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated 07.20.2011 No. ED-4-3 / 11684. There are two ways to define this part.
OPTION 1. We recover only VAT from the advance payment set off against a separate delivery under the terms of the contract
This option allows you to postpone the restoration of part of the advance VAT.
Here is the rationale for this approach, which has already found support in court e:
- tax recovery is necessary so that the buyer does not take into account the amount of VAT twice as deductions;
- vAT is subject to recovery, determined on the basis of the amounts that, according to the results of the period, cease to be an advance payment. For the same amounts that remain in advance (that is, are not set off against the delivery received), VAT cannot be recovered. And in the situation we are considering, after the first delivery, part of the prepayment continues to remain in advance;
- the amount of VAT that needs to be restored depends on the terms of the agreement on payment and offset of the advance, since the concept of prepayment is not defined in the Tax Code of the Russian Federation and the special procedure for offsetting the advance for VAT is not established;
- the procedure for offsetting the advance stipulated by the terms of the contract is obligatory for its parties, and the tax authorities are not entitled to either change this procedure or apply any other.
However, keep in mind that the inspection may not agree with such a recovery of VAT. But the arbitration practice has not yet developed. We know only one such dispute that has reached the court: the court took the side of the taxpayer, who restored the VAT in installments as the contract was executed in proportion to the amounts of the advance payment to be credited and Decision of the AC of Moscow dated May 31, 2011 No. A40-22038 / 11-140-101. The court clearly indicated that it is necessary to take into account the terms of the contract and restore the VAT only from that part of the prepayment, which in accordance with them ceased to be an advance upon shipment. And only when the procedure for offsetting the advance payment is not specified in the contract, the VAT should be restored within the amount of tax indicated by the seller in the shipping invoice.
Example. Recovery of advance VAT from the buyer with option 1
/ condition / We use the conditions of the previous examples.
/ decision / In the II quarter of 2011, the result of the first stage was accepted for accounting and the invoice of the contractor was received for it.
The customer in the II quarter restores the VAT deduction from that part of the advance payment, which under the terms of the contract is credited as payment for the first stage, that is 64 800 rubles. The rest of the deduction is 151,200 rubles. - he will restore later, when he takes into account the result of the second stage of work and receives an invoice from the contractor for it.
OPTION 2. We restore the VAT deduction in the amount indicated in the invoice for the goods received
First, compare the cost of goods received and the total amount of the advance:
- <если> the advance amount is greater, then we deduct the advance VAT deduction in the amount of VAT indicated by the seller in the shipping invoice issued to you, the rest is postponed for later (until the next delivery, against which the advance is credited);
- <если> the advance amount is less, then we deduct the advance VAT deduction in full.
Reader's opinion
“We restored the advance VAT in stages - in proportion to the part of the advance, which is offset against the payment of the adopted stage. And the inspectors who came with the check believed that it was necessary to restore the entire deduction immediately - when accepting the results of the first stage of work. They were about to sue, but - good luck! - they managed to repay the additional charges by filing an appeal to the Federal Tax Service. ”
Ekaterina Rogova,
lawyer
Judging by the letters from our readers, some field inspectors adhere to this order.
It turns out that for VAT, the advance payment is offset against the payment of goods received in an amount equal to the cost of the first delivery (or in whole if it is less than this value). But when you, following the terms of the contract, finally pay for this batch, the total amount transferred to the seller of money will exceed the cost of the goods received. And overpayment, again only for VAT purposes, will become an advance. Is it possible to deduct tax from it? No, even if the seller issues an advance invoice. After all, you will not have other conditions necessary for VAT deduction:
- mention of such an advance to the contract e section 9, Art. 172 of the Tax Code;
- instructions for prepayment in payment e section 12, Art. 171, clause 9, article 172 of the Tax Code, because in it you indicate that you are transferring money to pay for the delivery, and not an advance.
Example. Recovery of advance VAT from the buyer under option 2
/ condition / We use the conditions of the previous example.
/ decision / In the II quarter of 2011, the customer accepted the result of the first stage for accounting and received an invoice from the contractor.
The cost of the first stage (1,534,000 rubles) is more than the total amount of the advance payment (1,416,000 rubles). Therefore, the customer restores all advance VAT, that is, 216,000 rubles.
In the III quarter, the customer transfers 1,109,200 rubles, including VAT 169,200 rubles, to the contractor to pay off his debt for the accepted result of the first stage of work.
In total, at this moment, the contractor was transferred 2,525,200 rubles. (1 416 000 rubles before the start of work + 1 109 200 rubles in the III quarter as payment for the first stage). This is 991,200 rubles. (2 525 200 rub. - 1 534 000 rub.) More than the cost of the adopted result of the first stage.
Even if the contractor will consider these 991,200 rubles for VAT purposes. as the advance payment made in the third quarter of the second stage of work and invoices it, the customer will not be able to safely accept VAT from it for deduction.
This option is disadvantageous, because you will have to immediately restore all advance VAT, despite the fact that you pay for the delivery minus only part of the advance.
How can a buyer reduce the risk of a dispute with an inspection and not recover all VAT at once
It must be done so that it clearly follows from the contract, payment orders and advance invoices that a certain amount of prepayment is an advance on account of a particular delivery. For this:
- transferring an advance payment, make a separate payment for each part of it. In the purpose of the payment, indicate: “advance payment of the first (second, third, etc.) delivery under such an agreement”;
- ask the seller (or better yet, stipulate in the contract) that he:
Compiled a separate advance invoice for each part of the advance payment. After all, inspectors check deductions and recoveries primarily on invoices, sales and purchase books;
In the invoice for each delivery, he separately indicated the amount of the advance credited to the account of this delivery.
WARNING THE HEAD
Without emergency it’s better not to “smear” the advance payment paid for the entire period of execution of the ongoing contract (for all deliveries). It is better to agree with the seller on making an advance immediately before each delivery. Otherwise, there may be difficulties with VAT: either you will have to pay a lot of tax at once, or the inspection will have claims.
Of course, this is not always convenient. For example, in the case when under the lease agreement for 2 years the advance is credited in installments on a monthly basis, you would have to make 24 payments on it and ask the landlord to issue 24 invoices.
Moreover, in some cases this is not possible. For example, when the part of the advance that is credited to the account of each delivery is determined as a percentage of its value, and the cost at the time of the prepayment is still not known exactly (as, for example, happens in construction).
So, the tax authorities proceed from the fact that the seller, taking the tax for deduction, is obliged to take into account the terms of the contract for the gradual credit of the advance payment, and the buyer, restoring the tax, must ignore them. Fair this state of affairs can not be called. Indeed, if each of the parties to the contract chooses a safe option for itself, then after the next delivery for the time necessary to fulfill the remaining obligations under the contract, the budget receives the “excess” amount of VAT. All this time, such a seller’s VAT will not yet be deductible, and the buyer will already have it recovered.
The composition of the indicators of the invoice issued upon receipt of advance payment (partial payment), provided for in paragraph 5.1 of Art. 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Moreover, the special form of invoices issued in respect of advance payment (partial payment) has not been approved. Therefore, sellers of goods (works, services, property rights) when they are used use the invoice form approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation N 914, with the reflection in it of indicators provided for by the above norm.
In accordance with paragraphs. 4 p. 5.1 Art. 169 on account of the forthcoming deliveries of goods (performance of work, provision of services, transfer of property rights), the name of the delivered goods (description of works, services), property rights shall be indicated.
When filling out this indicator of the invoice should be guided by the name of the goods, property rights specified in the agreements concluded between the seller and the buyer.
For example, in case of receipt of advance payment (partial payment) under contracts for the supply of goods, providing for their shipment in accordance with the application (specification), drawn up after payment, in these contracts, as a rule, the generalized name of the delivered goods (for example, petroleum products, confectionery , bakery products, stationery, etc.). Therefore, when issuing an invoice when receiving an advance payment (partial payment) under such agreements, the generalized name of the goods (or their groups) should be indicated.
If contracts are concluded that provide for the execution of work simultaneously with the delivery of goods, the name of the delivered goods and a description of the work performed shall be indicated in the corresponding column of the invoice.
Upon receipt of advance (partial) payment under contracts for the supply of goods, taxation of which is carried out at rates of both 10 and 18%, the general name of the goods should be indicated in the invoice with the rate 18/118 indicated, or the goods should be allocated to separate items based on information contained in the contracts, indicating the appropriate tax rates.
When issuing an invoice for advance (partial) payment received under contracts providing for different delivery times for goods, the amount of this payment should not be allocated to separate items.
According to paragraph 3 of Art. 168 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation upon receipt of the amounts of payment (partial payment) against upcoming deliveries of goods sold in the territory Russian Federation, relevant invoices are issued no later than five calendar days, counting from the date of receipt of the indicated amounts.
If within five calendar days, counting from the day of receipt of the advance payment (partial payment), the goods are shipped on account of this payment (partial payment), the buyer should not issue invoices for such payment.
Upon receipt of payment (partial payment) on account of the forthcoming deliveries of goods by a commission agent (agent), who is selling goods on his own behalf within the framework of a commission (agency) contract, an invoice for this payment is issued to the buyer by a commission agent (agent), and the principal (principal) issues to the agent (agent) the invoice, which reflects the indicators of the invoice issued by the agent (agent) to the buyer. In this case, the commission agent (agent) of the invoice for payment (partial payment) on account of the forthcoming deliveries of goods issued by him to the buyer does not register in the sales book.
When making a payment (partial payment) against upcoming deliveries of goods (work, services, transfer of property rights), corresponding invoices are also issued in non-cash form.
Under contracts for the supply of goods (provision of services), providing for features related to the continuous long-term supply of goods (provision of services) to the same buyer (for example, the supply of electricity, oil, gas, the provision of communication services), draw up invoices for payment (partial payment) received on account of such deliveries of goods (provision of services), and expose them to customers, in our opinion, is possible at least once a month no later than the 5th day of the month following the expired. In this case, invoicing should be done by suppliers in tax periodwhen the amount of the preliminary (partial) payment is received. This procedure is possible, since the Tax Code does not define the concept of payment (partial payment), therefore, in this case preliminary (partial) payment can be considered the difference formed at the end of the month between the received amounts of payment (partial payment) and the cost of shipped this month goods (services provided).
According to the Ministry of Finance of Russia, such invoices should indicate the amount of the advance received in the corresponding month for which goods (services) were not shipped this month (Letter of 03.03.2009 No. 03-07-15 / 39). Upon receipt of payment (partial payment) against upcoming deliveries of goods (work, services) subject to taxation zero rate, and also not taxed by this tax, invoices are not issued.
The above Letter also contains another conclusion: in the case of the administration of VAT regarding tax recovery previously accepted for deduction when transferring payment (partial payment) for upcoming deliveries of goods, the tax authorities, according to the Ministry of Finance, should take measures tax control, similar to those carried out during checks of the amount of tax to be recovered when using previously purchased goods (works, services, property rights) to carry out operations subject to taxation at a zero rate, as well as operations not subject to this tax.
According to paragraph 12 of Art. 171 of the Tax Code of the taxpayer who transferred the amount of payment (partial payment) on account of the upcoming deliveries of goods, the tax amount claimed by the seller of these goods upon receipt of such amounts of payment (partial payment) are deductible. Paragraph 9 of Art. 172 of the Code established that these deductions are made on the basis of invoices issued by sellers upon receipt of advance payment (partial payment), documents confirming the actual transfer of these amounts, and if there is an agreement providing for their transfer.
If the contract for the supply of goods (performance of work, rendering of services, transfer of property rights) stipulates a condition for transferring a preliminary (partial) payment without specifying a specific amount, VAT should be deductible calculated on the basis of the amount of the transferred preliminary (partial) payment specified in invoice issued by the seller. If the condition on advance (partial) payment is not stipulated in the contract or the corresponding agreement is absent, and advance payment is transferred on the basis of the invoice, the tax on the transferred preliminary (partial) payment is not deductible.
When making a preliminary (partial) cash payment in cash or in a non-cash form, tax is not deductible, because in these cases the buyer of goods (work, services, property rights) does not have a payment order.
According to paragraph 1 of Art. 171 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, when calculating the amount of VAT payable to the budget, the taxpayer has the right to reduce the total amount of tax calculated on operations recognized as an object of taxation by the appropriate tax deductions. Consequently, the Tax Code of the Russian Federation provides for the right of a taxpayer to deduct VAT on the transferred amounts of advance payment (partial payment), and not the obligation to accept the tax for deduction. Thus, if a taxpayer uses his right to deduct tax on received goods (work, services), and not on advance payment (partial payment) of these goods, this, according to experts of the Ministry of Finance of Russia, does not lead to underestimation tax base and the amount of tax payable to the budget.
Difficulties that may arise in tax authorities when checking the correctness of the application of these deductions, they are not grounds for the impossibility of implementing the introduced system in practice, and even more so for refusing, as indicated in the Letter, tax control. the federal law dated November 26, 2008 N 224-ФЗ was adopted as part of the anti-crisis measures, and the procedure he introduced for deduction of VAT paid as part of payment (partial payment) for upcoming deliveries of goods is aimed at reducing tax burden on the relevant taxpayers and should not lead to an increase in the load (both tax and administrative) on VAT payers engaged in the sale of goods (works, services). In accordance with Art. 35 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, tax and customs authorities are liable for losses incurred by taxpayers, payers of fees and tax agents as a result of their unlawful actions (decisions) or inaction, as well as unlawful actions (decisions) or inaction officials and other employees of these bodies in the performance of their official duties.
- (Payment) Types and purpose of payments Cash on delivery and payment order Contents Content Section 1. Types. Section 2. Cash on delivery. Section 3 Payment order. Payment is the issuance of an obligation, transfer ... ... Encyclopedia of the investor
Payment order - A payment order (eng. Payment order) is an order of the account holder (payer) to the bank serving it, executed settlement document, transfer a certain amount of money to the account of the recipient of funds opened in this or another ... ... Wikipedia
Payment order - A form of a payment order A payment order is an order of the account holder (payer) to the bank serving it, drawn up by a settlement document, to transfer a certain amount of money to the account of the payee, about ... Wikipedia
A-conto Great Law Dictionary
A-conto - (from it. a conto in the invoice / payment /; English a conto) partial payment on account of the debt whose maturity date has come. The amount due to the creditor is recorded in the account (conto, compte) of the person for whom it is listed. So this person ... ... Encyclopedia of Law
Sales book - sellers keep a sales book designed to register invoices drawn up by the seller in transactions recognized as objects that are subject to value added tax, including non-taxable ones ... ...
Book of purchases - Buyers must keep a purchase book designed to register invoices issued by sellers in order to determine the amount of value added tax shown for deduction (reimbursement) in the prescribed manner. Invoices, ... ... Encyclopedic dictionary-reference of the head of the enterprise
Payment order - used for partial payment of a payment order by a bank. A partial movement (both receipt and write-off) of funds under a settlement document is reflected using this document. When placing a payment order for partial payment at all ... ... Wikipedia
- (payment on account) 1. Payment for goods and services delivered prior to the final invoice. See also: deposit. 2. Partial payment against obligation. In the customer’s books, the amount paid is credited to the account ... Glossary of Business Terms
PAYMENT TO ACCOUNT OF PAYABLE AMOUNT - (payment on account) 1. Payment for goods and services delivered prior to the final invoice. See also: deposit. 2. Partial payment against obligation. In the payer's books, the amount paid is credited to his ... Financial vocabulary
payment of due amount - 1. Payment for goods and services delivered prior to the final invoice. See also: deposit. 2. Partial payment against obligation. In the payer's books, the amount paid is credited to his account as partial ... ... Technical Translator Reference
Hello!
Regarding the method of receiving your invoice, I inform you that Art. 434 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation allows for the possibility of concluding a contract in writing by exchanging documents by post, telegraph, teletype, telephone, electronic or other communication, which makes it possible to establish reliably that a document comes from a party under a contract.
By virtue of Art. 433 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, the contract is recognized as concluded at the time of receipt by the person who sent the offer of its acceptance.
According to Art. 435 of the Code, an offer is recognized as an offer addressed to specific persons, which is quite definite and expresses the intention of the person who made the offer to consider himself to have concluded a contract with the addressee who will accept the offer. The offer must contain the essential terms of the contract. Thus, if the terms of the contract are specifically defined in the invoice, it can be considered as an offer.
In accordance with Art. 438 of the Code, acceptance is the response of the person to whom the offer is addressed, on its acceptance. In this case, the person who received the offer, within the time period established for its acceptance, takes actions to fulfill the conditions of the contract specified in it, incl. payment of the appropriate amount shall be considered an acceptance, unless otherwise provided by law, other legal acts or not indicated in the offer.
In addition, the deadline for your organization to pay the bill is important to answer your question. If the invoice has a deadline for payment, the contract is considered concluded if the payment was received by the person who sent the invoice within the time period indicated in it.
According to legal position Supreme Court RF and Higher Arbitration Court Of the Russian Federation, expressed in Decree No. 6/8 of July 1, 1996, “On Certain Issues Related to the Application of Part 1 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation,” “... it must be borne in mind that, along with the answer to the complete and unconditional acceptance of the conditions of the offer , shall be recognized that the person who received the offer, within the time period established for its acceptance, takes actions to fulfill the conditions of the contract specified in it, unless otherwise provided by law, other legal acts or the contract (clause 3 of Article 438). It should be borne in mind that in order to recognize the appropriate actions of the addressee of the offer by acceptance, the Code does not require that the terms of the offer be fully met. For these purposes, to qualify these actions as an acceptance, it is enough for the person who received the offer (including the draft contract) to proceed with its execution on the conditions specified in the offer and within the time period established for its acceptance. ”
Thus, having partially paid the bill, your organization entered into a purchase and sale agreement with the seller of the equipment.
By virtue of Art. 450 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, amendment and termination of the contract are possible, as a general rule, by agreement of the parties. At the request of one of the parties, the contract may be amended or terminated by a court decision only if there is a material breach of the contract by the other party or in other cases provided for by laws or the contract, in particular, if the circumstances change significantly.
In this situation, the choice the right option behavior is entirely dependent on an analysis of factual circumstances. After studying the contents of the account, the due date, the name of the payment, it will be possible to determine the prospects for recovering the money paid by your organization from the seller of the equipment as unjust enrichment, or filing a lawsuit to terminate the contract and determine the consequences of termination.
To attract and retain regular customers, companies are ready to provide them with goods and services at reduced prices. Sometimes sellers spend special promotionsto declare or remind about themselves, and during their action invoice at a discount. A sample of its design and the procedure for filling in the required details can be found in this article.
Discount regulation
Lowering the previously declared value of a product or service is called a discount. The Civil Code in the section on sales contracts (30th chapter) does not limit the seller in determining its size. However, organizations should be aware of the restrictions provided by the Tax Code.
Employees of the fiscal department have the right to verify the correctness of the set price if it deviates from the usual cost by more than 20% (Article 40 Tax code) And if they find such a big discount illegal, suspecting the seller of intentionally understating tax base, companies can accrue not only the tax itself, but also penalties. Moreover, their size will be calculated from the average rather than reduced price.
To avoid disputes with tax authorities, experts advise in writing to justify the provision of generous discounts in excess of 20%, and prepare a number of documents. In particular, organizations may come in handy:
- a document on the accounting policy of the company, where one of the sections determines the possible marketing moves;
- the head’s order on a significant reduction in the value of goods with an expiring shelf life;
- approved price lists with discount prices;
- written informing the buyer about the discount provided, etc.
The written justification of the high discounts, in particular, recommends clarifying that they are designed to promote new products on the market or are associated with a seasonal decrease in consumer demand for products that the supplier needs to sell in the shortest possible time.
Discount invoice: sample
The discounted account has a number of required details:
- name of the document (“ACCOUNT”), its number and date;
- name of the seller;
- her location; contacts;
- BIC, account numbers (correspondent, settlement);
- name of the bank;
- name of the buyer - organization or individual entrepreneur;
- name and quantity of goods sold;
- unit;
- cost / price of goods;
- amount of discount;
- total amount payable;
- signatures of officials.
The following is an example of processing such an account.
Sample discount invoice
Partial invoice payment
In practice, situations are common when the buyer does not immediately pay the full cost of the purchased goods, but makes an advance payment. Partial payment of the invoice is executed with the same details of the table, however, the data entered into it is reduced in proportion to the amount advanced. The invoice also indicates the amount of the discount.



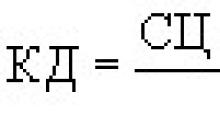





How to calculate the average annual value of fixed assets?
Socio-economic and domestic political development of the country
Signs of a postindustrial society, general characteristics and basic types What are the characteristics of a postindustrial society? Analyze the data
2 what are the objects of accounting
Map from the Pridonskaya microdistrict to Voronezh