Enter or edit the values \u200b\u200bof the main details compulsory sale orders :
In field room change the document number if necessary. By default, the system numbers the documents in the order they were created during the calendar year.
In field date if necessary, change the date of the document. By default, the field is populated with the current date.
Type of transaction indicate the type of free currency sale transaction. Values \u200b\u200bare selected from the list.
In field Spanish indicate the name of the artist. The value in the field can be set manually or selected from employee reference using the button.
In field tel. if necessary, indicate the phone number of the contractor.
If the creation of this document is based on existing in the system notifications of crediting funds to a transit currency account go to step 8 of this instruction. Otherwise, continue with the instructions.
In field From the amount received enter / edit the amount of received foreign exchange earnings.
Field excluding expenses automatically filled in with the amount of allowed costs based on documents justifying transaction costs indicated on the tab Additionally pages .
In field please debit from transit account indicate the transit account number. The account number value can be set manually or selected using the button.
After choosing a transit account number, all fields of the document’s currency codes are filled in automatically.
In field the amount indicate the amount debited from this account.
Field for the implementation of compulsory sale and the fields associated with it are not available for filling, as currently, on the basis of instruction No. 111-I of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation, the mandatory sale of part of residents' foreign currency earnings is carried out in the amount of 0 percent of the foreign currency earnings.
When generating a document for the free sale of received foreign currency earnings in the field for free sale indicate the amount of sale of the received foreign currency earnings.
When preparing a document for transferring received foreign currency earnings to a bank account:
When preparing a document for the free sale of foreign currency earnings:
By default, the fields of the number and date of the reservation statement are not editable, since this moment, in accordance with the law, there is no reservation requirement.
Go to the tab Additionally pages New Mandatory Currency Sale Order .
Fig. 4.70. Tab Supporting documents pages New Mandatory Currency Sale Order

If necessary, create a list of documents substantiating the allowed expenses:
Field Total allowed expenses incurred automatically filled with the amount of allowed costs based on list documents Documents substantiating transaction costs incurred from a transit currency account .
Click the button on the page toolbar All orders for the mandatory sale of currency (see Fig. 4.66 ).
The page will open. New order for the mandatory sale of foreign currency.
Fig. 4.67. Page New currency transfer order

A number of window fields will already be filled in by the system.
| Attention! | |
|---|---|
If necessary, create a list of documents substantiating the transaction:

CURRENCY REVENUE SELLING PROCEDURE
Organizations engaged in foreign economic activity receive in payment of their goods (work, services) sold abroad, foreign currency.In order to fully and timely receive export earnings, the state exercises control over the foreign economic activity of organizations.
Mandatory sale of a portion of residents' foreign exchange earnings in the domestic market Russian Federation in accordance with Article 21 of the Federal Law of December 10, 2003 No. 173-ФЗ "On Currency Regulation and Currency Control" (hereinafter Law No. 173-ФЗ) is implemented by residents - legal entities and residents - individuals who are individual entrepreneurs.
The requirement for the obligatory sale of part of the foreign exchange proceeds remains until January 1, 2007, the marginal norm of compulsory sale established by law is 30 percent, however, the Central Bank of the Russian Federation has the right to establish a different standard within these limits.
Instruction of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation dated March 30, 2004 No. 111-I "On the mandatory sale of part of foreign exchange earnings in the domestic foreign exchange market Of the Russian Federation "(hereinafter referred to as Instruction No. 111-I) it is established that the following foreign currency is subject to mandatory sale in the amount of 25 percent of the amount of foreign exchange earnings:
- Australian dollar;
- Danish krone
- Euro;
- Icelandic krona;
- Yen;
- Canadian dollar
- Norwegian Krone;
- Singapore dollar;
- Turkish lira;
- Pound sterling;
- Swedish krona
- Swiss frank.
- amounts in foreign currency received by the Government of the Russian Federation, authorized by federal executive bodies, the Central Bank of the Russian Federation from operations and transactions carried out by them (or on their behalf and (or) at their expense) within their competence;
- amounts in foreign currency received by authorized banks from their banking operations and other transactions, in accordance with the Federal Law "On Banks and Banking Activities";
- residents 'foreign currency earnings within the amount necessary to fulfill residents' obligations under loan agreements and loan agreements with non-resident organizations that are agents of foreign governments, as well as loan and loan agreements concluded with residents of member states of the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (hereinafter OECD) and the Financial Action Task Force on the Development of Anti-Money Laundering (FATF) for a period of more than two years;
- amounts in foreign currency received from transactions involving the transfer of external issue valuable papers (rights to external equity securities).
- payment for transportation, insurance and freight forwarding;
- payment of export customs duties, as well as customs duties;
- pay commission fee credit organizations, as well as payment for the performance of agent functions currency control;
- other expenses and payments on operations, the list of which is determined by the Central Bank of the Russian Federation.
In accordance with Chapter 2 of Instruction No. 111-I, for the mandatory sale of part of the foreign currency earnings of residents, authorized banks open a current foreign currency account for residents on the basis of a bank account agreement. At the same time, a transit currency account is opened, to which are credited to in full all receipts of foreign currency in favor of the resident. An exception is the following amounts credited to the current currency account, bypassing the transit:
- moneycoming from one current foreign currency account of a resident opened with an authorized bank to another current foreign currency account of this resident opened with this authorized bank;
- funds received from an authorized bank in which a resident's current currency account is opened, according to agreements concluded between them;
- funds received from the current currency account of one resident to the current currency account of another resident opened with one authorized bank.
The procedure for the mandatory sale of part of foreign exchange earnings in the domestic foreign exchange market of the Russian Federation is established by Chapter 3 of Instruction No. 111-I.
Not later than a business day following the day of receipt of foreign currency in a transit currency account of a resident, an authorized bank shall send him a notification. The notification must contain information on which account the currency proceeds were received, the amount and the date of crediting, the last date the bank submits an order for the mandatory sale of proceeds and a certificate identifying the amount of received currency indicated in the notification by type foreign exchange transactions, including the identification of foreign exchange earnings, which is the subject of compulsory sale, as well as other information.
Signed by the bank's responsible person, the notification with the statement of the transit currency account statement is sent to the resident.
No later than the day specified by the bank in the notification, the resident must give the bank an order to obligatorily sell part of the foreign currency proceeds, transfer the amount received in the currency of the Russian Federation to his bank account, transfer the amount of foreign currency left after the obligatory sale to his current foreign currency account or bank account in foreign currency.
An order of a resident legal entity is signed by two persons entitled to sign settlement documents, or by one person (in the absence of a second person in the state who can be granted the right to sign), declared on the card with specimen signatures and a seal, with the seal of the resident legal entity. An order of an individual entrepreneur - resident is signed by an individual - individual entrepreneur with a print application (if available).
A statement identifying the amount of received currency indicated in the notification by types of foreign exchange transactions, including identification of foreign exchange earnings, which is the subject of compulsory sale, is filled out in the manner and in the form established by Instruction No. 117-I.
Not later than the business day following the day of receipt of the order and the certificate from the resident, the authorized bank shall deposit the amount of foreign currency specified in the order from the resident's transit currency account to a separate personal account. Within two business days following the day of crediting foreign currency to this personal account, the bank must sell it.
Simultaneously with the deposit of foreign currency, the bank deducts from the transit currency account the remaining part of the foreign currency and transfers it to the current or transit currency account of the resident indicated in the order.
The bank account agreement between the authorized bank and the resident may stipulate that the resident has the right not to submit an order in each case, as well as that the authorized bank independently fills in the certificate.
The exchange between the authorized bank and the resident of the provided documents can be carried out by post, telegraph, teletype or other communication in the manner agreed between the authorized bank and the resident.
In the case of using facsimile reproduction of a signature by means of mechanical or other copying, electronic digital signature or another analogue of a handwritten signature between an authorized bank, on the one hand, and a resident, on the other hand, the procedure for recognizing an analogue of a handwritten signature is established, and the procedure terms of use.
ACCOUNTING AND TAX ACCOUNTING FOR THE SALES OF CURRENCY REVENUE
Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation of October 31, 2000 No. 94н "On approval of the chart of accounts accounting financial and economic activities of organizations and instructions for its use "(hereinafter the chart of accounts), to summarize information on the availability and movement of funds in foreign currencies in the currency accounts of the organization opened in credit organizations on the territory of the Russian Federation and beyond its borders, account 52 "Currency accounts" is provided.
Operations on foreign currency accounts are reflected in accounting on the basis of statements of credit organizations and the monetary settlement documents attached to them.
To account 52, sub-accounts are opened:
52-1 "Currency accounts within the country";
52-2 "Foreign currency accounts".
To reflect the movement in foreign currency by types of foreign currency accounts, it is necessary to open second-order sub-accounts:
52-1-1 "Current foreign currency account";
52-1-2 "Transit currency account";
52-1-3 "Special transit currency account."
In accordance with the Chart of Accounts, the receipt of export foreign currency earnings to the organization’s transit currency account is reflected in the debit of account 52 “Currency accounts” in correspondence with the credit of account 62 “Settlements with buyers and customers”.
Entries in the accounting records of the organization’s currency accounts, as well as of operations in foreign currency, are made in rubles in the amounts determined by converting the foreign currency at the Central Bank rate of the Russian Federation on the date of the transaction. At the same time, these entries are made in the currency of settlements and payments. Such a requirement follows from paragraph 24 of the Regulation on accounting and reporting, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated July 29, 1998 No. 34n "On approval of the regulation on accounting and reporting in the Russian Federation".
The list of dates for certain transactions in foreign currency is given in the Appendix to the Accounting Regulation "Accounting for Assets and Liabilities, the Value of which is Expressed in Foreign Currency", approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated January 10, 2000 No. 2n "On Approving the Accounting Position" Accounting for assets and liabilities whose value is expressed in foreign currency “PBU 3/2000” (hereinafter PBU 3/2000). In accordance with this list, the date of a banking transaction is the date the funds are credited to the currency account or debited from the organization’s currency account with a credit institution.
The funds written off by the bank on behalf of the organization from the transit currency account in foreign currency are reflected on the debit of account 57 "Transfers in transit" in correspondence with the credit of the corresponding subaccount of account 52 "Currency accounts".
The write-off of the value of the sold foreign currency is reflected in the debit of account 91 “Other income and expenses”, subaccount “Other expenses” in correspondence with the credit of account 57 “Transfers in transit”.
If in the period between the dates of the transaction there will be a change in the foreign currency exchange rate, the organization shall recalculate the value of funds in foreign currency. The resulting positive and negative exchange rate differences, in accordance with paragraph 13 of PBU 3/2000, are included in non-operating income or non-operating expenses and are reflected in the debit of account 91 “Other income and expenses”, sub-account 91-1 “Other income” and sub-account 91-2 " Other expenses "respectively.
Funds in rubles received from the sale of foreign currency are credited to the organization’s bank account specified in the order for the sale of export earnings. These amounts in accordance with paragraph 7 of PBU 9/99, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated May 6, 1999 No. 32n “On approval of the accounting regulations“ Organization revenues ”, are recognized as operating income. Operating income is reflected in account 91“ Other income and expenses ", sub-account 91-1" Other income "in correspondence with the debit of account 51" Settlement accounts ".
Commission to the bank for the sale of foreign currency is a service provided by credit organizations. Such expenses according to clause 11 of the Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated May 6, 1999 No. 33n "On approval of the accounting provision" Expenses of the organization "PBU 10/99" are operating expenses. The operating expenses are reflected in the debit of account 91 “Other income and expenses”, subaccount 91-2 “Other expenses” in correspondence with the credit of account 76 “Settlements with various debtors and creditors” and are confirmed by the bank statement. The deduction of the amount of the commission by the bank is reflected in the entry on the debit of account 76 “Settlements with various debtors and creditors” and the credit of account 51 “Settlement account”.
For the purpose of calculating income tax, the amount of the commission paid to the bank, which is an expense on the services of banks, on the basis of subparagraph 15 of paragraph 1 of Article 265 Tax code Of the Russian Federation (hereinafter referred to as the RF Tax Code) is included in non-operating expenses.
Example.The organization sold for export finished products. The contracted value of the product is $ 14,000.
Export proceeds in full were received on the organization’s transit account on August 5. The organization submitted an order to the authorized bank on the mandatory sale of export earnings and on the transfer of the remaining amount of foreign currency earnings to the current foreign currency account on August 6. The funds from the sale of foreign currency proceeds were credited on the day of its sale on August 9 to the organization’s bank account. The commission to the bank for the sale of export earnings amounted to 2,000 rubles.
To reflect operations on accounting accounts, let us assume that the dollar exchange rate remained constant and amounted to 29.20 rubles.
Account Correspondence Amount, rubles Contents of operation Debit Credit 52-12 62 408 800 Export revenue received (14,000 x 29.20) 57 52-12 102 200 Written off foreign currency for compulsory sale (14,000 x 25%) x 29.20 51 91-1 102 200 Credited to the current account funds from the mandatory sale of export revenue (3,500 x 29.20) 91-2 57 102 200 Written off the value of the sold foreign currency (3,500 x 29.20) 76 51 2 000 Written off a bank commission for the sale of foreign currency 91-2 76 2 000 Reflected commission expenses 52-11 52-12 306 600 Reflected the transfer of the remaining part of foreign currency earnings to the current foreign currency account (14,000 - 3,500) x 29.20 The end of the example.
Organization, execution and accounting of bank operations for the purchase and sale of non-cash foreign currency
CHAPTER 4. Accounting for transactions on the purchase and sale of non-cash foreign currency (for example, Alfa Bank)
Foreign exchange operations are regulated by the law "On Currency Regulation and Currency Control", adopted in October 1992. The law defines the principles of currency transactions in the Russian Federation, the powers and functions of currency regulation and currency control bodies, the rights and obligations of legal and individuals in relation to the possession, use and disposal of currency values.
The subjects of currency relations are divided by law into two categories: residents and non-residents.
Residents include:
individuals with a permanent residence in the Russian Federation;
legal entities established in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation, with location in the Russian Federation;
enterprises and organizations that are not legal entities, established in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation, with a seat in the Russian Federation;
diplomatic and other official representations of the Russian Federation located outside the Russian Federation;
branches and representative offices of residents located outside the Russian Federation.
Non-residents include:
individuals with a permanent residence outside the Russian Federation, including those temporarily located in the Russian Federation;
legal entities established in accordance with the legislation of foreign states with a location outside the Russian Federation;
enterprises and organizations that are not legal entities, established in accordance with the legislation of foreign states, with a location outside the Russian Federation;
foreign diplomatic and other representations located in the Russian Federation, as well as international organizations, their branches and representative offices;
branches and representative offices of non-residents located in the Russian Federation.
The object of currency regulation are operations carried out with currency values. According to the law, currency values \u200b\u200binclude:
foreign currency;
securities in foreign currency - payment documents (bills, checks, letters of credit, etc.), stock values \u200b\u200b(shares, bonds), and other debt instruments denominated in foreign currency;
precious metals - gold, silver, platinum and platinum group metals in any condition and form, with the exception of jewelry and other household products, as well as scrap of these products;
natural gems in raw and processed form, with the exception of jewelry and other household products from these stones and scrap of these products.
Operations with currency values \u200b\u200bare divided into two types: current currency transactions and operations related to the movement of capital.
Current currency transactions include:
transfers to the Russian Federation and from the Russian Federation of foreign currency for settlements without installment payments for the export and import of goods, works and services, as well as for settlements related to lending to export-import operations for a period not exceeding 90 days;
obtaining and providing financial loans for a period of not more than 180 days;
transfers to the Russian Federation and from the Russian Federation of interest, dividends and other income on deposits, investments, loans and other operations related to capital flows;
non-commercial transfers to and from the Russian Federation, including transfers of amounts salary, pensions, alimony, inheritance, as well as other similar operations.
Currency transactions related to capital flows include:
direct investment, i.e. investments in authorized capital enterprises with the aim of generating income and obtaining rights to participate in the management of the enterprise;
portfolio investments, i.e. purchase of securities;
transfers in payment of property rights to buildings, structures and other property, as well as other property rights;
provision and receipt of a deferred payment for a period of more than 90 days for the export and import of goods, works and services;
granting and obtaining financial loans for a period of more than 180 days;
all other foreign exchange transactions that are not current currency transactions.
Law in general view determines the procedure for conducting currency transactions by residents and non-residents. In detail, the rules for conducting currency transactions are established by instructions and other normative documents The Central Bank of the Russian Federation, which in accordance with the Law is a currency regulation body.
Currency values \u200b\u200bmay be at the disposal of residents and non-residents. Settlements between residents are carried out in the currency of the Russian Federation without restrictions. Settlements between residents in foreign currency may be carried out in cases permitted Central bank RF The sale of goods to citizens for cash foreign currency is prohibited. The right to sell goods (services, works) to citizens for foreign currency with receipt of payments by bank transfer or for cash foreign currency is granted by the Central Bank of the Russian Federation on the basis of the issuance of an appropriate license.
Foreign currency received by residents is required to be credited to their accounts with authorized banks. To open accounts abroad and credit foreign currency to them, residents must obtain a license (permit) from the Central Bank of the Russian Federation.
The currency received by residents as export earnings is subject to mandatory partial sale in the domestic foreign exchange market. Currently, the exporter is obliged to sell 50% of export foreign currency earnings in the domestic foreign exchange market.
Residents can buy foreign currency in the domestic foreign exchange market for current currency transactions. Current currency transactions are carried out by residents without restrictions. For residents to conduct operations related to the movement of capital, it is necessary to obtain a license from the Central Bank of the Russian Federation.
Non-residents can transfer, import and forward to the Russian Federation without restriction currency values in compliance customs regulations, as well as dispose of these values \u200b\u200bdomestically or transfer, export them abroad in compliance with customs regulations. The use by non-residents of the currency of the Russian Federation is regulated by the Central Bank of the Russian Federation.
Monitoring compliance with currency laws and currency regulation is carried out by currency regulation bodies, which include the Central Bank of the Russian Federation and the Government of the Russian Federation, as well as currency control agents, i.e. authorized banks.
An authorized bank is a bank that has received a license from the Central Bank of the Russian Federation for currency transactions. To obtain a currency license, a commercial bank must submit to the Central Bank of the Russian Federation copies of the charter and banking license, financial statements and the act of the last audit, an application for a foreign exchange license with business case the need for the bank to conduct foreign exchange operations indicating the expected types and volumes of such operations, a certificate of technical readiness of the bank to conduct operations in foreign currency, a certificate of qualified personnel, a certificate of the organization of internal banking control, etc.
The Central Bank accepts for consideration applications from commercial banks that have worked for at least one year, i.e. finished full fiscal year and prepared the official annual report.
The license issued by the Central Bank of the Russian Federation indicates the operations that are permitted to be performed by a commercial bank in foreign currency.
Analytical accounting of operations on accounts in foreign currency is carried out in two currencies: in the currency of the account - in foreign currency and in rubles at the official rate of the Bank of Russia.
Synthetic accounting is carried out only in rubles.
The list of currencies and their codes. The encoding procedure in the composition of analytical accounts opened in foreign currency.
With the introduction of the new accounting rules, the sections of balance and off-balance accounts were rejected. Now, foreign currency accounts are opened in all balance sheet and off-balance accounts where transactions in foreign currency can be taken into account. Personal accounts are opened in accordance with the currency and the currency code is indicated:
ruble - 810
brand - 280
dollar - 840
For international settlements and other operations in foreign currency, authorized banks establish correspondent relations with foreign banks and other authorized banks of the Russian Federation. When choosing foreign correspondent banks, preference is given to national banks, as well as large commercial bankshaving sustainable financial position and good business reputation.
Correspondent relations are drawn up through letters exchanged between banks, or through the conclusion of an agreement between them. In both cases, the procedure is established and the conditions for performing banking operations, opening and maintaining correspondent accounts are stipulated.
There are two types of correspondent relations: with the opening of correspondent accounts and without opening.
Correspondent accounts of authorized banks opened with other banks are called Nostro accounts, and the accounts of other foreign or authorized banks of the Russian Federation opened with this bank are called Loro accounts.
Correspondent accounts are opened in freely convertible currency and currency with limited conversion. The accounting of operations performed on the accounts of “Nostro” and “Loro” is reflected in separate accounts of the bank balance.
Transactions on Nostro accounts are recorded on balance accounts: 072 “Correspondent accounts with non-resident banks in freely convertible currency”, 080 “Accounts with non-resident banks of the Russian Federation in foreign currency”, 082 “Correspondent accounts with non-resident banks in foreign currency with limited conversion. "
Nostro accounts are active, they account for bank funds deposited with foreign correspondent banks and Russian authorized banks. From these accounts, bank payments are made in favor of foreign organizations, firms, banks and individual citizens, as well as payments in foreign currency between authorized russian banks. All payments from Nostro accounts are made only with the permission of the bank that owns the account and are issued by credit memos to correspondent banks with an indication of the value date. Foreign currency is credited to the Nostro accounts by correspondent banks independently, as reported to the bank-holder of the account. Loro accounts are recorded on balance accounts: 073 “Correspondent accounts of non-resident banks in freely convertible currency”: 081 “Accounts of resident banks of the Russian Federation in foreign currency”, 087 “Correspondent accounts of non-resident banks in foreign currency with limited conversion”. All specified accounts are passive; foreign currency belonging to correspondent banks is accounted for them. The credit of these accounts records the receipts of foreign currency owned by correspondent banks and their customers. The bank makes foreign currency credits independently with the notification of the correspondent bank. The debit of Loro accounts reflects payments in foreign currency in favor of this authorized bank and its customers. These operations are performed by an authorized bank with the permission of the correspondent bank.
According to the correspondent accounts “Nostro” and “Loro”, in the analytical accounting personal accounts are opened for each bank and type of currency.
Open personal accounts are registered with an authorized bank in the book of open personal accounts. Several correspondent accounts may be opened for one correspondent bank (by type of currency).
Operational accounting for each personal account It is kept in special cards in the currency of the account. Operational accounting records the documents correctly executed and corresponding to the account regime that are to be posted to balance accounts, provided that it is possible to make a payment.
Correspondent banks send out statements of accounts “Nostro” and “Loro” within the agreed time. An authorized bank checks the statements of Nostro accounts as they are received. Based on the results of the quittance of the amounts indicated in the extracts, with the data of the authorized bank accounting, a cancer-cord is prepared monthly (calculation reconciliation table). The need to compile a cancer cord is caused by the fact that the turnovers and balances of personal accounts on the statements of correspondent banks do not always coincide with the accounting data of an authorized bank. The authorized bank shall notify the correspondent bank of the discovered discrepancies and take measures to eliminate them.
Within the deadlines established by the correspondent agreement, correspondent banks accrue interest on the Nostro and Loro accounts. The amount of accrued interest in favor of the correspondent bank is reflected in the Loro account in correspondence with account 970 “Operating and miscellaneous expenses”. In the amount of accrued interest in favor of the authorized bank, the Nostro account is debited in correspondence with account 960 “Operating and miscellaneous income”.
The new Chart of Accounts in Credit Institutions for recording the accounting of operations on correspondent accounts of resident banks provides for the use of accounts 30109 “Correspondent Accounts of Credit Correspondent Organizations” (Loro Account) and 30110 “Correspondent Accounts in Credit Organizations-Correspondents” (account Nostro); for non-resident banks - accounts 30111 “Correspondent accounts of non-resident banks” (Loro account) and 30112 “Correspondent accounts in non-resident banks” (Nostro account).
To carry out foreign economic settlements in an authorized bank, both residents and non-residents open accounts in foreign currency.
To open a foreign currency account, the client provides the following documents to the bank:
1. An application for opening a current balance sheet currency account in the established form;
2. Application for opening a transit currency account;
3. A notarized copy of the charter or regulation on the activities of the enterprise; memorandum of association;
4. A notarized copy of the card with specimen signatures and the seal of the enterprise;
5. The decision to create or reorganize the enterprise;
6. References from the tax office, pension fundstatistics bodies on registration of an enterprise;
7. Documents on the election (appointment) of the head, chief accountant of the enterprise.
In connection with the mandatory sale of part of the currency by Russian legal entities in the domestic foreign exchange market, two parallel existing accounts are opened in an authorized bank for each client: current and transit.
In a foreign currency transit account, the full amount of receipts in foreign currency is credited.
The current foreign currency account takes into account the funds remaining at the disposal of the enterprise after the obligatory sale of export earnings.
The current foreign currency account in the bank is assigned a number. The currency of the account is determined by the client. Incoming funds are initially credited to the transit currency account. Direct crediting of funds to the current foreign currency account occurs after the mandatory sale of foreign exchange earnings.
In order to carry out resident purchases of foreign currency for rubles in the foreign exchange market by an authorized bank in parallel with the current foreign currency account and in a transit currency account, a special transit currency account shall be opened for the resident.
A special transit currency account is an account opened by an authorized bank without the participation of a resident in order to record the resident’s purchases of foreign currency in the foreign exchange market.
When opening a foreign currency account with a bank, the account mode is negotiated, i.e. the rights of the owner of an account both for crediting and debiting funds from this account. The bank must inform the account holder about the movement of foreign currency funds on it.
The bank may charge fees for maintaining a foreign currency account, the tariffs of which are set commercial bank by yourself. The bank may charge interest for storing currency in the current currency account.
The following are credited to the foreign currency accounts of enterprises: export revenue transferred from abroad for goods, work or services performed; currency purchased in the domestic market in accordance with applicable law; dividends, income in foreign currency; foreign currency deposits JV participants in the authorized capital.
Funds deposited in the current currency account may be ordered by the client:
* aimed at paying for imported goods, services rendered and work performed;
* used to pay off debt on loans received in foreign currency; for payment bank commissions and postal and telegraph costs; to pay for travel expenses;
* used for sale in the domestic market in accordance with applicable law.
Payments from the current currency account are made within the limits of the funds available on the account.
International payments for the export and import of goods are made only through banks. In foreign trade, such forms of payments are used as bank transfer, collection, letter of credit.
Settlement forms are the methods of registration, transfer and payment of shipping and payment documents that have developed in international commercial and banking practice.
The indicated forms of international payments are applied when making payments both in cash and on credit. In this case, bank transfers are used in cash settlements, a documentary letter of credit - in cash settlements and in the provision of short-term commercial loans, collection form - in cash payments and in settlements using a commercial loan.
The specific form of settlement, in which payments will be made under the foreign trade contract, is determined by agreement of the parties - partners in the foreign trade transaction and are indicated in the contract.
Bank transfer - an instruction of the bank to the entire correspondent bank to pay a certain amount of money to the request and at the expense of the remitter to the foreign recipient (beneficiary), indicating the method of reimbursing the paid sum to the paying bank.
Bank transfer is carried out by bank transfer through payment orders addressed by one bank to another. Commercial and shipping documents are sent with this form of payment from the exporter to the importer directly, i.e. bypassing the bank.
Operations:
1 - the exporter transfers to the importer documents on the shipment of goods provided for by the contract;
2 - the importer submits to the bank a statement of order for the transfer of money;
3 - the bank withdraws money from the account;
4 - the bank sends the money to the bank of the exporter;
5 - the exporter's bank credits money to the account of the supplier (exporter), debiting it from the account of the correspondent bank;
6 - transfer to the exporter of an extract from his account on the transfer of funds.
The payer (usually the importer) gives the bank an application for withdrawing money from its foreign currency account and transferring it by bank transfer to the account of the contracting party that shipped the products to him. The exporter (beneficiary) acts as a counterparty. Upon receiving such a statement, the bank servicing the payer withdraws money from its foreign currency account and credits it to the correspondent account of the correspondent bank serving the payee (Loro account in our bank). A set of documents of m / b turnover on the basis of which money is transferred to foreign bank. The latter credits to the account of the supplier - exporter, debiting the correspondent account of our bank (nostro) opened with him. In the calculations bank transfers usually requires the provision of commercial documents (contract). Most transfers are made through the SWIFT system, which provides a multiple increase in the speed of cash settlements.
A collection is an exporter’s order to his bank to receive from the importer a certain amount or confirmation (acceptance) that this amount will be paid in fixed time.
When conducting a collection operation, banks and their customers are guided by the Unified Collection Rules developed by the International Chamber of Commerce. The Unified Rules as amended by 1978 are currently in effect.
The unified rules determine the types of collection, the procedure for submitting documents for payment and making a payment, acceptance, the procedure for notification of payment, acceptance or non-payment, non-acceptance, determine the obligations and responsibilities of the parties, give a uniform interpretation of various terms and solve other issues.
According to the Unified Rules, collection is a transaction carried out by banks on the basis of instructions received, with documents in order to:
receipt of acceptance (payment);
issuance of commercial documents against acceptance and / or payment;
issuance of commercial documents on other conditions.
Depending on the types of documents with which the collection operation is carried out, there are two types of collection:
pure collection, i.e. collection of financial documents, which include checks, bills, payment receipts and other documents used to receive payment;
documentary collection, i.e. collection of commercial documents that may or may not be accompanied by financial documents.
When making export settlements in the form of documentary collection, the exporter, after the goods are shipped, presents a collection order to the authorized bank with the application of the goods documents provided for by the contract. A collection order is issued on the forms of the established form with the obligatory indication in it: the currency of payment, the procedure for transferring documents to the payer (after payment or after acceptance), the possibility of making partial payments, the order of transferring documents for partial payments. The collecting bank is obliged to strictly follow the instructions of the exporter.
The collection order must indicate:
date and number of the order;
name of the payer and his postal address;
name of the Russian seller organization;
a list of documents attached to the collection order and their copies;
the amount of foreign currency to be collected, with the obligatory indication of the currency of payment.
If the document is issued in one currency, and the payment is made in another, then the rate of conversion of one currency to another should be indicated in the collection order.
Collection order and other goods documents are sent to a foreign bank. Collection orders sent by an authorized bank are registered by country and are received on off-balance sheet account 9936 “Documents and valuables sent for collection” (91102 “Documents and valuables sent for collection to non-resident banks”). Copies of collection orders are placed in the card file for this account, which indicate the time period for receiving foreign currency. Upon receipt of a credit memo by a foreign bank about the payment made, the amount of the received currency is credited to the exporter's transit account with the simultaneous debiting of the foreign bank account. A collection order is written off to account 9936 (91102).
When making payments for imported goods, collection orders and goods documents received from foreign banks are registered by an authorized bank. A copy of the collection order and goods documents are issued to the payer in accordance with the instructions contained in the collection order. Imported goods are paid on the basis of an importer’s application for a currency transfer to a foreign bank for the exporter. Money in the amount of the transfer is debited from the current currency account of the importer and credited to the correspondent account of the exporting bank.
When making settlements on import operations, a payment claim with an appendix required documents arrives at an authorized bank, where the foreign currency account of the Russian importer is located. The documents also contain instructions to the authorized bank on the execution of the payment. Documents received by the bank are received in a special file cabinet on off-balance account No. 91102. Upon receipt of the documents, the importer's bank notifies the client that a collection order and related commercial documents have been received. When paying the bill, the client brings to the bank an application for the transfer of funds to the exporter three days before the due date. A copy of the application with a bank visa is returned to the client against receipt.
Typically, payment terms for payment documents are specified in contracts. If the deadlines are not specified, then the collection order is executed by the bank within two weeks from the date of receipt of the documents. When debiting funds from the clients' currency accounts, payment documents are simultaneously debited from the card file No. 90901/91103.
In the absence of funds on the client’s account, documents are transferred to the card file No. 90902 (late payment documents) and instructions of the foreign bank are requested.
In the collection order, the exporting company gives the foreign bank collecting the payment an exact indication of when it can transfer commercial documents for receiving the goods to the importer. Two cases are possible: the first - commercial documents are transferred to the importer after payment of the amount of currency specified in the collection order; the second - the goods are sold on credit, so the shipping documents are transferred to the importer against the acceptance of an urgent draft (bill). Prior to this, the documents remain the property of the bank.
TRATTA is a bill of exchange. Unlike a promissory note issued and signed by the debtor, a bill of exchange is issued and signed by the creditor. By writing out a bill of exchange (draft), the creditor (drawer) orders the debtor (drawer) to pay the amount indicated in the bill by the due date to a third party (remitter). This is usually an authorized exporter bank. In order for a transferable bill to have legal force (that is, the possibility to claim the amount indicated on it after the expiration of the bill of exchange with the debtor), the drawee must accept the bill. This operation, on behalf of the exporter, is carried out by an authorized bank serving the importer. Accepted draft means that the importer agrees to pay the goods delivered to him or the services rendered to him by the time indicated on the bill.
When performing these calculations, authorized banks are obliged to verify the timely payment by Russian importers of collection orders, acceptance of drafts, timely return of documents in case of full or partial refusal of acceptance.
Despite the widespread collection of payments for export-import transactions, it has disadvantages that reduce its advantages over other forms of international payments:
1. So, during export operations, there is a significant time gap between the shipment of goods, delivery of documents for collection and receipt of money for goods and services. The duration of the calculations slows down the turnover of funds from the exporter, which cannot but affect his financial situation.
2. Collection does not guarantee the exporter the timely receipt of funds. The importer may not have the means to pay, refuse to accept payment documents. To speed up the calculations, telegraphic collection is used.
To reduce the risk of non-payment for collection, pre-issued bank guarantees timely payment of collection orders. The bank receives a certain income for issuing a guarantee.
Letter of credit - an obligation of the bank to make, on behalf of and with the instructions of the importer, an export payment or acceptance of its draft (bill of exchange issued by the exporter, when making payments on credit) within a certain amount and period and upon submission of the agreed documents to the bank.
Documentary letter of credit - an obligation of a bank, issued by it on behalf of its importing client, to make a payment in favor of the exporter (to accept his drafts) or to ensure payment (acceptance of drafts) by another bank within a certain amount and within the established time period against the documents specified in the letter of credit.
In calculations for import and export, documentary letters of credit are used, payments for which are subject to the submission of commercial documents to the bank.
The use of letters of credit in international settlements is regulated by the Unified Rules and Customs for Documentary Letters of Credit developed by the International Chamber of Commerce. Since January 1, 1994, the Rules are in force as amended in 1993 (ICC publication 500). The rules are binding on the banks that have joined them and their customers making payments by letters of credit. Each letter of credit includes a clause that the Rules are an integral part of each such letter of credit.
The unified rules define the concept and types of letters of credit, the methods and procedure for their execution and transfer, the duties and responsibilities of banks, the requirements for documents presented under letters of credit and the procedure for their submission, give an interpretation of various terms, and also consider other issues that arise in the practice of settlements by letters of credit.
Different types of letters of credit may be used in the calculations.
Revocable letter of credit - letter of credit, which may be canceled or the terms of it changed by the issuing bank at any time without prior notice to the beneficiary. However, the issuing bank must provide the bank authorized to make the payment a refund if this bank made a payment against documents submitted by the beneficiary (or accepted these documents for payment by letter of credit with an installment plan) before receiving notification of the change of conditions or cancellation from the issuing bank revocable letter of credit.
An irrevocable letter of credit is a letter of credit that cannot be canceled and the terms of which cannot be changed without the consent of the parties concerned.
The application for the letter of credit should clearly indicate whether the letter of credit is revocable or irrevocable. The unified rules stipulate that if there is no such indication, then the letter of credit is considered irrevocable.
To increase the degree of guarantee of payment on a letter of credit in the calculations, confirmed letters of credit are used. Confirmation of a letter of credit means a guarantee of payment by another bank that is not the issuing bank. The bank that has confirmed the letter of credit assumes the obligation to pay for documents that comply with the terms of the letter of credit in case the issuing bank refuses to make a payment. In international practice, the confirming bank, as a rule, is the bank serving the exporter.
4.10.1 Actions on the order for the obligatory sale of currency The order on the obligatory sale of currency is intended for transferring the received foreign currency proceeds from the transit foreign currency account to the current foreign currency account. The remaining part of the revenue (but not less than the established percentage) is transferred to the bank account for compulsory sale.
An order for the mandatory sale of currency can
create
create from a template,
edit,
delete
look,
print out
sign,
send to processing,
withdraw.
4.10.2 How to create an order for the mandatory sale of foreign currency?
An order for the mandatory sale of currency can be created in several ways:
without using a template,
using the template.
To create a new order for the mandatory sale of currency without using a template, follow these steps:
A document form will appear on the right side of the window.

Figure 20 - The form of the document "Order for the mandatory sale of currency"
Indicate number document. By default, the document number is filled in according to auto-numbering.
Figure 21 - Documents substantiating the receipt of currency
Figure 22 - Justification of expenses
Select transit from the list score.
Indicate the amount debiting from a transit account.
Choose from the list score sales.
Enter the amount in percent or currency to be credited to the sales account.
Select from the list score.
Indicate the amount transfers to the current account.
Mark the item transfer the ruble proceeds from the sale to our account. Why put a checkmark in front of the field
in our bank
Select from the list score.
in another bank
Attention! The document must be saved. Unsaved documents are not received by the system!
The order on the obligatory sale of currency is used to carry out the obligatory sale of part of the organization's export revenue from its transit account.
In order to create an order on the mandatory sale of currency, go to Documents – Mandatory sale and click on the button Create. A form for creating a document will be displayed on the screen.
Create an order
To create an order, fill in the following fields:
- In order for the order number to be filled in automatically, check the box Auto. By default, the check box is selected.
- In field date indicate the date of creation of the document in the format DD.MM.YYYY. Field date By default, the current date is set.
- In field Notification No. indicate the number of the notification from the bank about the receipt of funds to the transit currency account of the client’s organization.
- In field date indicate the date of notification from the bank about the receipt of funds to the transit account of the client’s organization. Field date can be completed using the calendar. To do this, click on the icon next to the field and select the value you are interested in.
- In field TIN select the customer organization’s TIN from the list.
- In field Cont. face indicate the name, position, phone, fax, e-mail of the authorized employee of the organization - the client.
- In field Amount of revenue indicate the total amount of revenue. In the box next to, select the letter currency code from the list.
- In field Trans. score select the number of the transit account from which the currency is debited from the list.
- In field date indicate the date of receipt of foreign currency earnings in the transit account in the format DD.MM.YYYY. Field date can be completed using the calendar. To do this, click on the icon next to the field and select the value you are interested in.
- In the fields Transp. exp., Doc No. and date indicate the amount of expenses for transportation, insurance and freight forwarding, as well as the number of the document confirming the operation and the date of the operation. Field date can be completed using the calendar. To do this, click on the icon next to the field and select the value you are interested in.
- In the fields Customs exp., Doc No. and date indicate the amount spent on the payment of export customs duties, the number of the document confirming the transaction, and the date. Field date can be completed using the calendar. To do this, click on the icon next to the field and select the value you are interested in.
- In the fields Bank. exp., Doc No. and date indicate the amount of expenses for paying a commission to the bank, as well as the number of the document confirming the operation and the date of the operation. Field date can be completed using the calendar. To do this, click on the icon next to the field and select the value you are interested in.
- In the fields Other cons., Doc No. and date indicate the amount of other expenses, as well as the number of the document confirming the operation and the date of the operation. Field date can be completed using the calendar. To do this, click on the icon next to the field and select the value you are interested in.
- In field Charged Amount enter the amount of foreign currency debited from the transit account.
- In field Amount Exceeded. Enter the amount of foreign currency in excess of the amount of mandatory sale.
- In field % of sale indicates the percentage of sales revenue.
- In field Amount of sale enter the amount of foreign currency for the mandatory sale.
- In field Amount credited enter the transfer amount remaining from the mandatory sale of foreign currency.
- In field Code 138-I indicate the code value of the type of foreign exchange transaction at 138-I. The field can be filled using the directory. To do this, click on the button next to the field and select the desired value from the opened directory.
- In field Tech./special. score - current / special currency account to which the remaining currency from the mandatory sale is credited. The field can be filled using the directory. To do this, click on the button next to the field and select the desired value from the opened directory.
- In field BIC enter the BIC of the bank to the account of which the currency is transferred from the transit account. If you click on the icon next to the field, then the fields K / s and Bank
- In field Ruble account the ruble account of the client’s organization is indicated, to which the proceeds from the mandatory sale of currency are credited. The field can be filled using the directory. To do this, click on the button next to the field and select the desired value from the opened directory.
- In field BIC enter the BIC of the bank to the account of which the proceeds from the obligatory sale are credited. If you click on the icon next to the field, then the fields K / s and Bank automatically filled with data from the directory of banks. If the information is not in the directory, then the fields must be filled in manually.
- Foreign exchange earnings can be sold at the MICEX and at the bank's exchange rate. To select a value, select the field Sell \u200b\u200bon the MICEX or At the rate of the bank.
- In field Course enter the rate of compulsory sale of currency.
- In field date enter the value date. Field date can be completed using the calendar. To do this, click on the icon next to the field and select the value you are interested in.
- In the fields Reference No. and date enter the reference number identifying the amount of received currency indicated in the notification by types of currency transactions, and the date of the reference. Field date can be completed using the calendar. To do this, click on the icon next to the field and select the value you are interested in.
- In the fields Contract No. and date enter the number and date of the contract. Field date can be completed using the calendar. To do this, click on the icon next to the field and select the value you are interested in.
- In the fields Transaction Passport No. and date enter the number and date of the transaction passport. Field date can be completed using the calendar. To do this, click on the icon next to the field and select the value you are interested in.
- In the fields TBG number and date enter freight number and date customs declaration (GTE). Field date can be completed using the calendar. To do this, click on the icon next to the field and select the value you are interested in.
- In field Other specify other documents.
If you want to set the number manually, uncheck the box Auto and in the field Order No. enter the document number.
As a result of the field OKPO, Name and Address will be filled in automatically. If this information is not available in the directory, then specify the OKPO, name and address of the client’s organization manually.
After all the required fields are completed, click on the button Save. A document viewing form will open where you can sign and send the document to the bank.
If you want to clear the completed fields of the document, click on the button Clear.
In order to go to the filter / search without saving the entered information, click on the button Cancel.
Signing an order
Signing a document depends on the number of signatures required:
If you use SafeTouch or Antifraud Terminal smart card readers to confirm operations in the system, you can visually verify the signing of the document. After you click on the button Sign the document with the selected signature, the details of the document will be displayed on the device screen. In this case, the document will not be signed until you confirm the operation by clicking on the button with the “+” sign (or Ok).
Note: to work with these devices, you must connect them to your computer using the USB port and enter the requested PIN code into the smart card.
After signing, you can send the document to the bank.
Sending an order to the bank
To send a document to the bank, click on the button Send a document to the bank on the document view page. After that, the signed document will be transmitted to servicing bank for further processing and it will be assigned the status of "Sent to the bank."
You can track the further course of processing a document by its status in the list of documents.



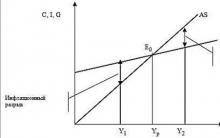





Where to invest a million rubles?
I am looking for an investment project
Real estate investment
Available online deposits in VTB
To whom and on what conditions they give a mortgage in a savings bank